A Handy Guide to The Profit and Loss Statement: How it helps Small Businesses

Small businesses should be able to track their finances closely to understand how the company is performing. Though cash flow statements or balance sheets are available, the profit and loss statement is one of the best ways to track financial performance. Read on for our handy guide to understand and decipher a Profit and Loss statement for small businesses.
Contents
What is a Profit and Loss Statement?
How do you read and analyze a profit and loss statement?
Components of a Profit and Loss Statement
Profit and Loss Statement vs. Balance Sheet
Benefits and Advantages of Understanding the Profit and Loss Statement
How Do You Analyze the Data in a Profit and Loss Statement?
How to Read Your Profit and Loss Accurately?
What can a Business Know from a Profit and Loss Statement?
What are the Alternatives to Profit & Loss Statements?
FAQs
What is a Profit and Loss Statement?
A Profit and Loss Statement, or a Profit and Loss or income statement, is a financial report that provides a snapshot of a company's revenue (Revenue Categories), costs (Expense Categories), and expenses over a specific period. The purpose of the profit and loss is to show whether or not a business is profitable and to what extent. The profit and loss statement can also be mentioned as an income statement, statement of income, financial results statement, earnings statement, or operations statement.
Example Profit and Loss Statement
Here is a sample Profit and Loss (P&L) statement for "Sweet Delights Bakery" for the year ending December 31, 2022.
Category | Amount |
Sales Revenue | $45,500.00 |
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) | $18,200.00 |
Gross Profit | $27,300.00 |
Operating Expenses | $32,500.00 |
- Employee Wages | $12,000.00 |
- Rent for Bakery | $6,500.00 |
- Utilities | $2,000.00 |
- Equipment Maintenance | $3,000.00 |
- Marketing and Advertising | $5,500.00 |
- Insurance | $2,500.00 |
- Office Supplies | $1,000.00 |
- Miscellaneous Expenses | $500.00 |
Depreciation Expense | $1,800.00 |
Interest Expense | $1,200.00 |
Earnings Before Income Tax | $22,800.00 |
Income Tax Expense | $9,000.00 |
Net Profit | $13,800.00 |
Here is the Bakery’s Financial Summary:
Sweet Delights Bakery had a sales revenue of $45,500.00 from selling baked goods. The cost of ingredients and materials (COGS) was $18,200.00. The gross profit after subtracting COGS was $27,300.00. Operating expenses, including employee wages, rent, utilities, and more, totaled $32,500.00. After accounting for depreciation and interest, the bakery had earnings before income tax of $22,800.00. The income tax expense paid to the government was $9,000.00. The bakery's net profit, or earnings after taxes, was $13,800.00.
Preparing the Profit and Loss Statement Using One of Two Methods:
Cash Method: The cash method (Cash Method), often known as the cash accounting technique, is utilized exclusively when actual cash flows are in the business. It is a fundamental system that only keeps track of money coming in and going out. When money comes into a company, it is considered revenue and a liability when it leaves the company. Smaller businesses and individuals in charge of their cash widely employ this approach.
Accrual Accounting Method: Accrual accounting (Accrual Accounting Method) tracks income as earned. The accrual technique accounts for future revenue. Even when unpaid, a firm that supplies a product or service counts revenue on its profit and loss statement. Corporations record liabilities even before they pay for costs.
Revenue categories on the Profit and Loss include sales, interest income, dividends, and investment gains. Expense categories include the cost of goods sold (COGS), selling, general & administrative expenses (SG&A), and interest expense. Net income (or net loss) is then calculated by subtracting total costs from total revenues (Net Income).
The profit and loss statement can be used to assess a company's financial performance over time or to compare it against other companies in its industry. It can also be used by management to decide where to allocate resources in the future, aiding in resource allocation and evaluating financial performance.
How do you read and analyze a profit and loss statement?
The Profit and Loss Statement often called the P&L Statement, is an essential tool for small business owners to track their company's financial performance. This guide will explain what information is found in a typical Profit and Loss Statement and how to use it to make better business decisions.
Components of a Profit and Loss Statement
As a small business owner, you must understand your company's financials strongly. You must know how to read and analyze a profit and loss statement.
A profit and loss statement, also called an income statement, is a report that shows your revenues, expenses, and net income for a given period. It's important to note that the term "net income" can also be referred to as "net profit" or "bottom line."
There are four main components of a profit and loss statement:
Revenue: The total amount your business has earned during the period covered by the profit and loss statement. Revenue can come from sales of goods or services, interest or investment income, or any other source.
Expenses: The total amount of money your business has spent during the period covered by the profit and loss statement. Expenses can include the cost of goods sold, selling, general and administrative expenses, or any other type of expense.
Net Income: The final profit and loss statement represents your business's profitability. Net income is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue.
Net Income = Total Revenue - Total Expenses
Profit and Loss Template: A profit and loss template is a standardized format for creating profit and loss statements. It provides a structured framework for presenting financial data and helps businesses organize their financial information for analysis and reporting.
Profit and Loss Statement vs. Balance Sheet
A profit and loss (profit and loss) statement, also known as a Profit and Loss or income statement, summarizes a company's revenues, expenses, and profits/losses over a given period. This essential financial document allows businesses to track their financial performance and determine whether they are operating profitably. It is a crucial tool for small business owners seeking to gain insights into their company's financial health and make informed decisions.
In contrast, a balance sheet offers a different perspective. A financial statement provides a snapshot of a company's financial position at a specific time. While a profit and loss statement focuses on the performance over time, a balance sheet reveals the company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a particular moment. This information is vital for assessing a company's financial stability and ability to meet its obligations.
Now, let's delve into the critical distinctions between a profit and loss statement and a balance sheet, exploring how each contributes to a comprehensive financial analysis:
Profit and Loss Statement | Balance Sheet |
- Tracks financial performance over time. | - Offers a snapshot of the company's financial position at a specific time. |
- Summarizes revenues, expenses, and profits/losses. | - Presents information on assets, liabilities, and equity. |
- Helps in pricing decisions and resource allocation. | - Evaluates a company's financial health and ability to meet financial obligations. |
- Identifies trends in revenue, expenses, and profitability. | - Considers the company's profitability and ability to cover loan payments. |
- Analyzes core operations, non-operating income, and expenses incurred. | - Analyzes all the costs, including raw materials and expenses related to core operations. |
- Evaluate the fiscal year's financial performance and prospects. | - Provides insights into public companies and their financial standing. |
- Measures business success and determines profitability. | - Examines the company's ability to manage future performance and handle specified periods. |
- Examines tax expenses, interest payments, and the company's profit. | - Offers a loss statement template for assessing financial performance. |
- Assists in calculating free profit and determining the company's ability to cover loan payments. | - Examines the role of accounting software in financial reporting. |
- Provides insights into all expenses, including indirect costs and overhead expenses. | - Explores the significance of cash equivalents in maintaining liquidity. |
- Highlights the importance of reporting periods and services sold. | - Expands the understanding of financial performance, resource allocation, and business success. |
Both profit and loss statements and balance sheets serve as invaluable tools for small business owners, helping them understand their company's financial status and make well-informed decisions for the future.
Benefits and Advantages of Understanding the Profit and Loss Statement
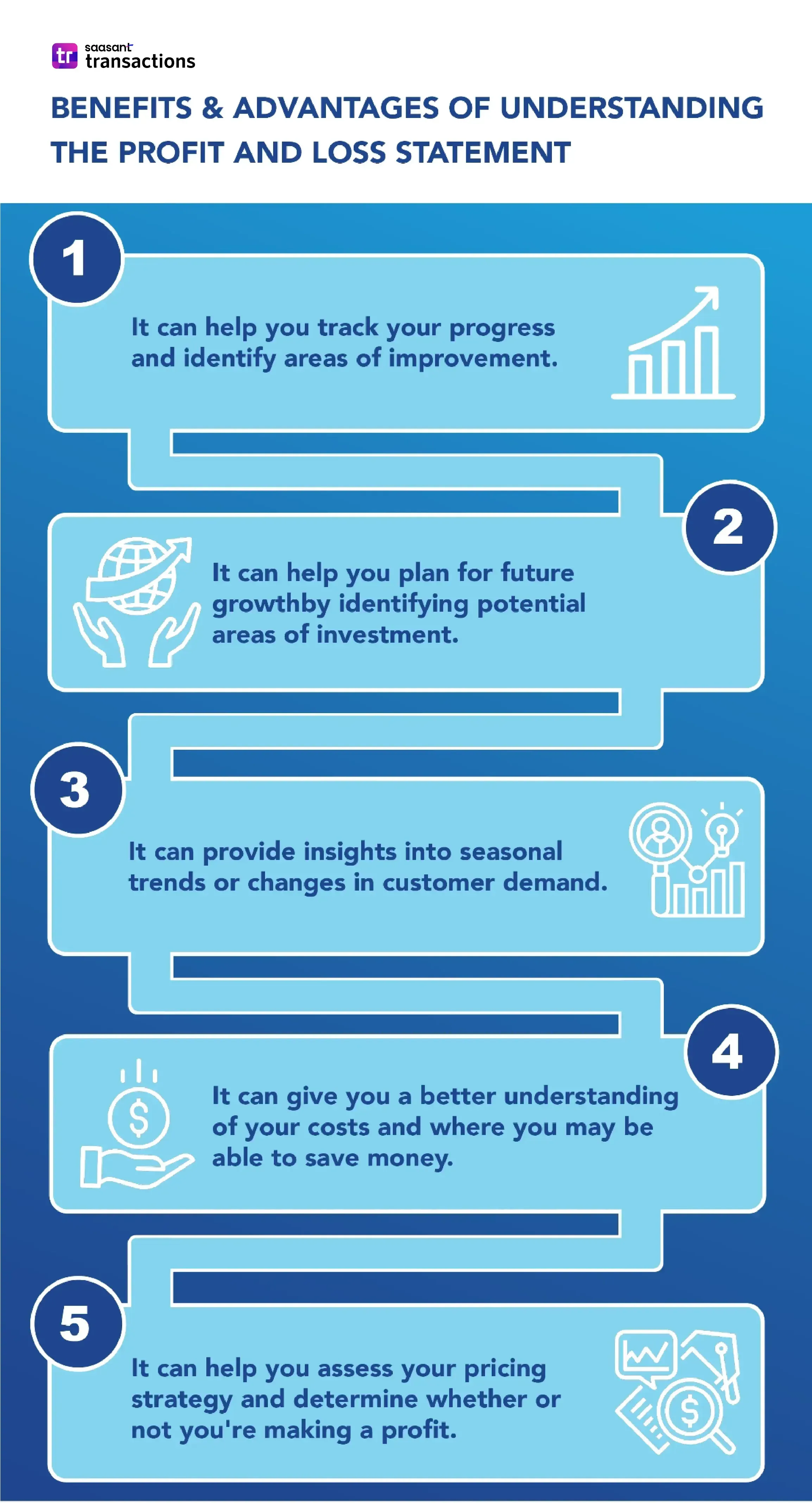
When running a small business, one of the most important things you can do is keep a close eye on your finances and understand your small business profit and loss statement.
Your profit and loss is a crucial financial document that outlines your revenue, expenses, and profits for a specific time. It can help you track your progress, identify areas of opportunity, and make more informed decisions about where to invest your resources.
There are many benefits and advantages to understanding your profit and loss. Here are just a few:
It can help you track your progress and identify areas of improvement.
It can give you a better understanding of your costs and where you can save money.
It can help you assess your pricing strategy and determine whether or not you're making a profit.
It can provide insights into seasonal trends or changes in customer demand.
It can help you plan for future growth by identifying potential investment areas.
How Do You Analyze the Data in a Profit and Loss Statement?

Assuming you have a basic understanding of the Profit and Loss Statement, analyzing the data within it can be daunting to small business owners. Where do you even start? Here are five tips on how to analyze the data in your Profit and Loss Statement:
Know your margins - It is essential to consider this in your Profit and Loss Statement. Your Gross Margin is your total revenue minus the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) divided by total revenue. It will give you a good idea of how much profit you're making on each sale. Ideally, you want a high Gross Margin (meaning you're making a lot of profit per sale).
Look at your operating expenses - These are the costs of running your business, like rent, utilities, marketing, etc. Keeping these costs in check is essential because they can eat into your profits quickly.
Analyze your customer acquisition costs - How much are you spending to acquire new customers? The number should be compared to the lifetime value of a customer to see if it's worth it.
Comparing with previous Profit and Loss Statements - When reviewing your Profit and Loss Statement year over year, compare similar periods (like month over month or quarter over quarter). It will give you a more accurate picture of your business's growth or decline.
Evaluate Net Income - Your Net Income is the final figure on your Profit and Loss Statement, representing your business's profitability. Monitoring this number is essential as it reflects your overall financial performance.
Analyzing your Profit and Loss Statement using these tips can provide valuable insights into your business's financial health and help you make informed decisions to improve profitability and efficiency.
How to Read Your Profit and Loss Accurately?
If you're like most small business owners, you only have a little experience reading financial statements. But if you want to keep your business in good financial health, it's essential to understand how to read your Profit & Loss (profit and loss) statement.
Here are some tips for reading your profit and loss accurately:
Know what you're looking at - The profit and loss statement is a financial document that shows your revenue, expenses, and profit for a specific period. Ensure you know when the profit and loss statement covers to interpret the numbers correctly.
The Right Way to Compare Statements - When comparing your profit and loss from one period to another, compare similar periods. For example, don't compare your profit and loss from January to March with your profit and loss from April to June. It will give you an inaccurate picture of your financial health. You must compare the profit and loss from January to March of one year with the profit and loss from January to March of another year. It ensures accurate tracking of financial performance over time and provides meaningful insights into trends and changes in your business's financial health.
Look at the Big Picture - Don't get too caught up in the details of each line item on the profit and loss statement. Instead, take a step back and look at the big picture, like net income, revenue trends, and expense management. It will help you identify any trends or red flags that may be present.
In addition to looking at your profit and loss statement, review your balance sheet and cash flow statement. These statements will offer valuable insights into your business performance, including expenses incurred, loss statement templates, and strategies for increasing revenue.
What can a Business Know from a Profit and Loss Statement?
A business can derive several valuable insights from a Profit and Loss (P&L) statement, which can help a business owner make informed decisions and manage the company's financial health. Some of these critical insights include:
Revenue Trends: The P&L statement shows the company's revenue over a specific period. Business owners can track revenue trends to assess if their sales are growing, stable, or declining. This information helps in forecasting future revenue and setting realistic sales goals.
Profitability: The P&L statement clearly shows the company's profitability. By comparing total revenue to total expenses, business owners can determine if the business is making a profit or incurring losses. Understanding profitability is crucial for sustainable growth.
Expense Management: The breakdown of expenses in the P&L statement allows business owners to identify areas where costs can be controlled or reduced. It helps in optimizing expenses, which can lead to higher profitability.
Gross Profit Margin: Calculating the gross profit margin (gross profit divided by total revenue) reveals how efficiently a company produces goods or services. A higher gross profit margin indicates that the company generates more profit from each sale.
Operating Efficiency: By analyzing operating expenses, business owners can assess the efficiency of day-to-day operations. Reducing unnecessary operating expenses can improve the bottom line.
Income Tax Planning: The P&L statement shows the income before taxes. Business owners can use this information for tax planning and to set aside the appropriate amount for tax liabilities.
Cash Flow Management: While the P&L statement doesn't directly show cash flow, it can indirectly impact cash flow by revealing patterns in revenue and expenses. Understanding these patterns helps in managing cash flow effectively.
Resource Allocation: Business owners can use the P&L statement to allocate resources to areas of the business that need them the most. For example, if marketing expenses drive revenue growth, allocating more resources to marketing can be beneficial.
Investor and Lender Relations: Investors and lenders often review P&L statements to assess the financial health of a business. A positive P&L statement can attract investors and help secure loans or financing.
Strategic Planning: The insights gained from a P&L statement are invaluable. Business owners can make informed decisions about expansion, cost-cutting measures, pricing strategies, and overall business direction.
Comparative Analysis: By comparing P&L statements from different periods, businesses can track progress and identify areas of improvement. Year-over-year or quarter-over-quarter comparisons provide a historical perspective.
Identifying Seasonal Trends: Some businesses experience seasonal fluctuations in revenue and expenses. Analyzing the P&L statement can help business owners anticipate and prepare for these variations.
What are the Alternatives to Profit & Loss Statements?
Not every business uses the traditional profit and loss statement. Some enterprises use alternatives like the cash flow statement or the Statement of Changes in Equity. These statements can give you a different perspective on your business's financial health.
The cash flow statement shows how much cash is coming from your business. It can be helpful if you're trying to manage your cash flow or are concerned about needing more money to cover your expenses.
The Statement of Changes in Equity shows how your equity has changed over time. It can be helpful if you're trying to understand your business’s value or considering selling it.
Understanding and keeping track of a Profit & Loss Statement is vital for any company and can provide valuable insights into the financial performance of your business. With some effort, you can use these facts and figures to make informed decisions that will help drive your business forward. So, get started today and make sure you are on top of your Profit & Loss statement.
If you want to learn more about finding marginal cost, check out this guide how to find marginal cost.
FAQs
What is on a profit and loss statement?
A profit and loss statement, often called a P&L statement or income statement, is a financial document that summarizes a company's revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period. It typically includes information such as total revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, and net profit. This statement helps businesses assess their financial performance by showing whether they are making a profit or incurring losses during the specified period.
What is a simple statement of profit or loss?
A simple statement of profit or loss, also known as a primary income statement, is a financial report that outlines a company's earnings and expenses within a given time frame. It includes revenue from sales or other sources, subtracts the cost of goods sold (if applicable), and then deducts operating expenses. The result is the net profit or loss, which reflects how much money the company has made or lost during that period.
Is P&L the same as an income statement?
Yes, P & L (Profit and Loss) is the same as an income statement. Both terms are used interchangeably in accounting and finance to describe a financial document summarizing a company's revenues, expenses, and overall profitability for a specified period. The purpose and content remain consistent whether you refer to it as a P&L or an income statement.
How do you summarize a profit and loss statement?
To summarize a profit and loss statement effectively, follow these steps:
Start with the total revenue: Begin by identifying the total income generated by your business from sales, services, or other sources.
Deduct the cost of goods sold (COGS): Subtract the direct costs of producing goods or services, such as materials, labor, and manufacturing expenses, from the total revenue.
Calculate gross profit: Determine the gross profit by subtracting the COGS from the total revenue. It represents the profit generated from core business operations.
Account for operating expenses: List and deduct all operating expenses, including rent, utilities, marketing, salaries, and administrative costs.
Find the net profit or loss: Subtract the total operating expenses from the gross profit to arrive at the net profit (if positive) or net loss (if negative).
Present the final figure: Summarize the net profit or loss at the bottom of the statement. A positive number indicates profitability, while a negative number reflects a loss.