What is Accounts Receivable? AR Process, AR Automation, and AR Turnover Ratio Explained

No matter how big or small your business is, understanding stuff like Accounts Receivable (AR) and Accounts Payable (AP) is essential for keeping your finances in check. These are like the balance sheet superheroes showing how your business is performing. Ignoring these two is like missing a piece of the puzzle that could mess up your financial game.
Whether you’re grinding through CPA training or running a business, getting the basics right is critical. AR is money owed to you, while AP is what you owe others. Knowing these can help you monitor your cash flow and determine your business's financial standing.
So, let’s explore AR: what it does, how it works, and why distinguishing it from AP is a big deal.
Contents
What is Accounts Receivable?
Using Technology to Manage Accounts Receivable (AR)
Financial Metrics and Reports
Strategies to Reduce Overdue Payments
Conclusion
What is Accounts Receivable?
Accounts Receivable (AR) refers to the money a business owes its customers for goods or services that have been delivered but are yet to be paid. It represents the outstanding invoices or amounts receivable from clients or customers.
AR is a crucial asset on the balance sheet because it represents the money the business expects to receive shortly. AR is essential to a company's working capital and overall financial health.
Now, let's contrast Accounts Receivable with Accounts Payable (AP). While AR represents money owed to the business by its customers, AP refers to the money that the business owes to its suppliers or vendors for goods or services received but still needs to be paid. In simple terms, AR is what others owe to the business, whereas AP is what the company owes to others. Understanding this difference is crucial in managing cash flow effectively and assessing the financial position of a business.
The Accounts Receivable Process Explained
The Accounts Receivable (AR) process begins with a credit sale and concludes with the receipt of payment. Here's an overview of the steps involved:
Credit Check & Approval: Before extending credit to a customer, businesses typically conduct a credit check to assess the customer's creditworthiness. If approved, credit terms are agreed upon.
Sale & Invoicing: Once a sale is made on credit, an invoice is generated detailing the products or services provided, their quantities, prices, and payment terms.
Sending the Invoice: The invoice is sent electronically or by mail to the customer, specifying the payment due date and any discounts or penalties for early or late payment.
Recording the Sale: Upon sending the invoice, the sale is recorded in the company's accounting system as an account receivable, reflecting the amount the customer owes.
Payment Tracking: The business monitors payments received against outstanding invoices, tracking the progress of each customer's payments.
Payment Recording: When a customer makes a payment, it is recorded in the accounting system, reducing the outstanding balance of the accounts receivable.
Reconciliation: Regular reconciliation ensures that the AR balance in the accounting records matches the actual receivables outstanding from customers.
Ageing Analysis: The AR ageing analysis categorises outstanding receivables by the time they have been excellent (e.g., current, 30 days past due, 60 days past due, etc.), helping identify overdue accounts.
Reporting: Reports are generated regularly to provide insights into AR balances, ageing, collections, and outstanding payments. These reports aid in decision-making and assessing the effectiveness of credit policies and collection efforts.
Actions on Non-payment: In cases of non-payment or overdue accounts, businesses may take actions such as sending reminders, initiating collection calls, offering payment plans, or ultimately resorting to legal action or writing off bad debts.
By following these steps and effectively managing the AR process, businesses can ensure timely payment receipt, maintain healthy cash flow, and minimise bad debt risks.
Using Technology to Manage Accounts Receivable (AR)
The effective management of Accounts Receivable (AR) is significantly enhanced by technology, streamlining processes, improving accuracy, and enhancing overall efficiency. Here’s a deeper look into the benefits of automating AR and an introduction to using applications like SaasAnt PayTraQer.
Benefits of Automating Accounts Receivable (AR)
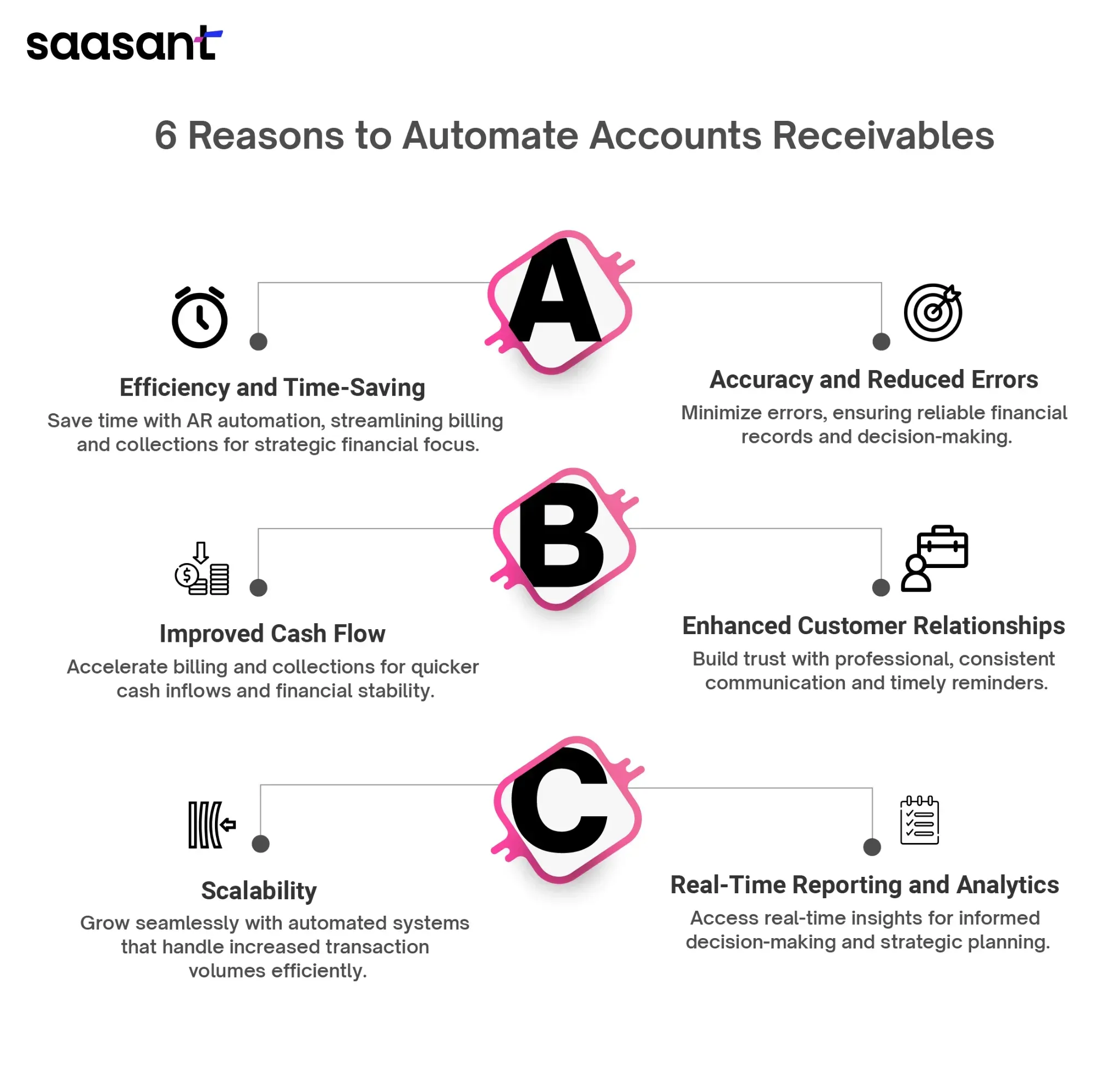
Efficiency and Time-Saving: Automation reduces the manual tasks associated with AR management, such as data entry, invoice generation, and payment tracking. This speeds up the entire AR process from billing to collections, freeing up valuable time for focusing on strategic financial activities.
Accuracy and Reduced Errors: Automated systems minimise human errors in invoice creation, data entry, and account reconciliation. This leads to more accurate financial records, ensuring financial reporting and decision-making reliability.
Improved Cash Flow: Automation helps businesses improve their cash flow by accelerating the billing and collections processes. Faster invoice processing and prompt payment tracking mean quicker cash inflows.
Enhanced Customer Relationships: Automation provides more consistent and professional communication with customers regarding their invoices and payments. Automated reminders and clear, timely correspondence can improve customer satisfaction and help maintain healthy business relationships.
Scalability: Automated AR systems can easily adjust to handle increasing volumes of transactions without the need for additional staff. This scalability makes it easier for businesses to grow and manage increased demand without compromising financial control and customer service.
Real-Time Reporting and Analytics: With automated tools, businesses gain access to real-time data and analytics, providing up-to-date insights into AR performance, customer payment behaviour, and financial health. This information is crucial for strategic planning and operational adjustments.
Simplify the Management of Account Receivables
Use SaasAnt Transactions, an innovative application designed to simplify and automate the management of Accounts Receivable processes. It integrates seamlessly with accounting systems like QuickBooks, making it a robust solution for businesses of all sizes. Key features include:
Invoice Automation: SaasAnt Transactions automates creating and sending invoices, reducing manual errors and saving time for finance teams. It can generate invoices in bulk, customise templates, and schedule recurring invoices for seamless billing cycles.
Payment Reminders: The application sends automated payment reminders to customers, reducing late payments and improving cash flow. Customisable reminder schedules ensure timely follow-ups without manual intervention.
Multi-Currency Support: For businesses dealing with international clients, SaasAnt Transactions supports multi-currency transactions, simplifying AR management for global operations. It automatically converts currencies based on real-time exchange rates.
Integration with Payment Gateways: Seamlessly integrate with popular payment gateways like PayPal, Stripe, or Square to streamline payment processing. This integration enables customers to pay invoices directly online, accelerating payment collection.
Customer Communication: Enhance customer communication with personalised messages, thank-you notes, and updates on outstanding balances. Maintain a positive relationship with customers while efficiently managing AR processes.
Real-Time Dashboard: Monitor AR performance in real-time with interactive dashboards displaying key metrics like outstanding balances, ageing receivables, and payment trends. Identify bottlenecks and take proactive measures for improved cash flow management.
Automated Reconciliation: SaasAnt Transactions automates the reconciliation process by matching payments received with corresponding invoices in the accounting system. This reduces errors and ensures accurate financial reporting.
Compliance and Security: The application adheres to data security standards, providing encrypted data storage and secure access controls. It also helps businesses stay compliant with accounting regulations and audit requirements.
Financial Metrics and Reports
Understanding and tracking specific financial metrics and generating regular reports are vital for analysing the health of your Accounts Receivable. Key metrics to monitor include Days Sales Outstanding (DSO), Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio, and the percentage of accounts beyond the due date. These metrics provide insights into how quickly your business collects cash and can influence financial strategies and policies.
Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): This metric shows the average number of days receivables remain outstanding before being collected. A lower DSO indicates faster collections, improving cash flow.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: This ratio measures how often, on average, your receivables are collected during a period. A higher turnover ratio suggests more efficient collection processes.
Percentage of Accounts Beyond Due Date: Tracking this metric helps identify potential issues in the payment process or credit policy effectiveness.
Regularly generating reports based on these metrics can help identify trends, prepare for financial obligations, and ensure that cash flow remains steady. These reports can be integral in strategic planning and operational adjustments.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio: Definition and Formula
The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a key financial metric used to assess how effectively a company manages and collects debts from its customers. It measures how often a business can convert its accounts receivable into cash over a specific period. The formula to calculate this ratio is:
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio=Net Credit Sales/Average Accounts Receivable
Net Credit Sales refer to the total revenue from sales made on credit minus any returns or allowances.
The Average Accounts Receivable is calculated by adding the accounts receivable at the beginning of the period to the accounts receivable at the end and then dividing by two. Depending on the period being analysed, this average could also be calculated monthly, quarterly, or annually.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio and Financial Health

The accounts receivable turnover ratio is crucial for evaluating a company's liquidity and operational efficiency. Here’s why it’s significant:
Efficiency in Collections: A higher ratio indicates that the company is efficient in collecting debts from its customers, which means it is quickly turning receivables into cash. This is important as faster collections help ensure the business has enough cash to meet its financial obligations.
Credit Policy Insights: This ratio can provide insights into the company's credit policies. A lower ratio might suggest that a company's credit terms are too lenient, potentially leading to cash flow issues. On the other hand, a very high ratio might indicate strict credit policies, which could discourage potential sales.
Liquidity: The ratio highlights the liquidity aspect of the company's operations. Businesses with a high turnover ratio are generally more capable of covering short-term liabilities and expenses without securing additional financing.
Trend Analysis: Tracking this ratio over time helps understand trends in the company's credit control and collections processes. Fluctuations in the ratio can alert management to potential issues in sales, customer satisfaction, or the efficiency of the collections department.
Benchmarking: Comparing this ratio against industry standards or key competitors can provide a relative sense of how well the company manages its receivables. It's important for investors and creditors to assess relative performance and financial health.
Understanding and managing the accounts receivable turnover ratio can significantly impact a company's cash flow and financial stability. It is a vital tool for financial analysis and planning, ensuring businesses can continue operating smoothly without running into liquidity issues.
AR Aging Schedule: Explanation and How to Create One
An AR Aging Schedule, or accounts receivable ageing report, is a critical financial tool that categorises a company's accounts receivable according to the time an invoice has been outstanding. This report helps businesses identify invoices that are overdue for payment and assess the effectiveness of their credit and collection efforts.
How to Create an AR Aging Schedule?
List all outstanding receivables: Start by listing all the invoices yet to be paid by customers. Include the invoice number, customer name, date, and total amount.
Categories by age: Divide the outstanding invoices into categories based on how long they have been unpaid. Common categories are 0-30 days, 31-60 days, 61-90 days, and over 90 days overdue.
Calculate total per category: Sum the total amount outstanding in each category. This clearly shows how much is owed within each time frame.
Update regularly: The ageing schedule should be updated frequently (typically weekly or monthly) to reflect current data. This ensures the company has an accurate view of the status of its accounts receivable.
Integrate with accounting software: Many businesses use accounting software that automatically generates an ageing schedule, which helps reduce errors and saves time.
Importance in Managing Overdue Payments:
Prioritising collections: The ageing schedule helps businesses prioritise their collection efforts. By focusing on older debts first, companies can manage their cash flow more effectively and reduce the likelihood of accounts becoming uncollectible.
Identifying trends: Regular analysis of the AR Aging Schedule can help identify trends in payment behaviour. For example, if a significant amount of receivables consistently fall into the 60-90 day category, this might indicate a need to reassess the company's credit terms or collection processes.
Improving customer relationships: Businesses can more proactively manage customer accounts by monitoring the ageing schedule. Reaching out to customers before their invoices become overdue can help maintain good customer relationships and prevent future payment issues.
Mitigating credit risk: The schedule provides crucial information about customers' creditworthiness. Businesses can use this data to adjust credit policies or limit future sales to customers with poor payment histories.
Financial planning: Understanding the timing of cash inflows from receivables is essential for effective financial planning. The ageing schedule helps ensure no surprises in cash flow, allowing for better management of business operations and investment decisions.
Strategies to Reduce Overdue Payments
Reducing overdue payments is crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow and minimising financial risk. Here are some strategies that can help:
Clear Communication: Ensure that your payment terms are clearly defined and communicated at the start of any customer relationship. Ambiguities can lead to delays in payment.
Incentives for Early Payment: Offering discounts can motivate customers to pay sooner than the due date.
Regular Follow-ups: Implement a system for regular follow-ups before and after the invoice due date. Timely reminders can prevent overdue payments.
Flexible Payment Options: Providing multiple payment methods makes it easier for customers to settle their invoices.
Credit Management: Assessing a customer’s credit risk before extending credit can prevent issues. Adjust credit terms based on the customer's payment history and creditworthiness.
Conclusion
This discussion explored crucial aspects of accounts receivable (AR) management, focusing on the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio and the AR Aging Schedule. These tools are indispensable for evaluating how effectively a company manages its receivables and ensuring that sales made on credit are converted into cash efficiently.
The Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio provides insights into the frequency with which receivables are collected during a given period. A higher ratio indicates better efficiency in collections, which directly impacts a company's liquidity and operational effectiveness. Conversely, the AR Aging Schedule offers a detailed look at the age of outstanding invoices, helping businesses prioritise collections and identify potential issues in their credit policies.
Effective AR management is essential for maintaining robust cash flow, minimising credit risk, and ensuring financial stability. Companies are encouraged to adopt best practices in managing receivables, such as regular reviews of AR reports, proactive customer communications, and stringent credit controls. Additionally, integrating modern tools and accounting software can streamline the process, reduce errors, and provide real-time insights into the business's financial health.
Read also:
QuickBooks Online Accounts Receivable: Your In-Depth, Practical Guide to Getting Paid