Small Business Growth: Challenges and Success Strategies

Small businesses are integral to the economy, serving as hotbeds of innovation, engines of job creation, and cornerstones of local communities. Despite their significant contributions, these enterprises often grapple with unique challenges on their path to growth and success. In this quick blog, let us get into the intricacies of small businesses, exploring the hurdles they face, the stages they traverse in their growth journey, and ten invaluable success strategies that empower them to thrive in a fiercely competitive area.
Small business owners encounter several obstacles, from limited resources and the quest to acquire and retain customers to the complexities of corporate social responsibility. However, their resilience, adaptability, and the strategic application of success strategies can propel them towards sustainable growth.
Contents
What is a Small Business?
Challenges Faced by Small Businesses
The Four Stages of Small Business Growth
10 Success Strategies for Small Businesses
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Small Business?
Before knowing the challenges and strategies, defining what constitutes a small business is essential. A small business is a privately owned entity with fewer employees and lower annual revenue than larger enterprises. Criteria for defining "small" vary by country and industry.
Small businesses comprise a significant portion of the economy in the United States, accounting for over 99% of all companies. They employ nearly half the private-sector workforce and generate about two-thirds of net new jobs annually. It underscores their critical role in nationwide economic growth, innovation, and job creation.
Small businesses are diverse, ranging from family-owned shops to innovative startups. Only 9% of small companies reach $1 million or more in revenue, and only 50% of businesses surpass the 5-year mark.
Challenges Faced by Small Businesses
While financial constraints top the chart regarding problems for small businesses, other areas can hinder the growth of entrepreneurs and innovative companies. Let us see about a few of them.
Limited Resources and Tight Budgets:
Challenge: Small businesses often need more financial resources and must operate on tight budgets. This constraint can hinder their ability to invest in essential areas necessary for growth, such as marketing, technology upgrades, and hiring talented personnel.
Strategies:
Prioritization: Small business leaders should prioritize spending on initiatives directly impacting growth and profitability. Assess which investments will provide the most significant return on investment (ROI).
Alternative Funding: Consider exploring options like small business loans and grants or seeking investors to secure additional capital for critical investments.
Acquiring New Customers:
Challenge: Identifying and attracting potential customers, especially in a competitive market, can be a massive challenge for small businesses.
Strategies:
Targeted Marketing: Focus on targeted marketing efforts that reach the right audience. Utilize data analytics and customer profiling to understand customer demographics and preferences.
Leverage Digital Marketing: Utilize digital marketing channels, such as social media advertising, search engine optimization (SEO), and content marketing, to increase online visibility and reach potential customers.
Networking: Attend industry-specific events and networking opportunities to connect with potential clients and partners.
Customer Retention:
Challenge: While acquiring new customers is crucial, retaining existing ones is equally vital. Customer loyalty is critical to long-term success.
Strategies:
Loyalty Programs: Implement customer loyalty programs that reward repeat customers with discounts, exclusive offers, or loyalty points.
Exceptional Customer Service: Prioritize exceptional customer service to build strong relationships with clients and address their needs promptly to improve customer retention.
Engagement: Engage with customers through email marketing, social media, and personalized communication to maintain a sense of community and loyalty.
Effective Marketing Strategies:
Challenge: Developing cost-effective marketing strategies that resonate with the target audience can be a constant challenge for small businesses with limited budgets.
Strategies:
Content Marketing: Create valuable and informative content that establishes your expertise and engages your audience.
Social Media Engagement: Leverage social media platforms to interact with your audience, share content, and run targeted ad campaigns.
Email Marketing: Build and nurture an email list to regularly engage with your audience through newsletters and promotions.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Challenge: Practicing CSR and giving back to the community can be challenging for small businesses with limited resources.
Strategies:
Local Engagement: Focus on local CSR initiatives that align with your business's values and mission. It could include supporting local charities, schools, or community events.
Partnerships: Collaborate with other businesses or organizations to pool resources and collectively support CSR initiatives.
Sustainability: Consider adopting sustainable business practices that benefit the environment and the community, such as reducing waste or supporting eco-friendly suppliers.
The Four Stages of Small Business Growth
In the journey of a small business, growth, and development occur in distinct stages. From its humble beginnings in the existence stage, where survival is the primary focus, to the exhilarating take-off stage marked by rapid expansion, and finally, the pinnacle of success, where profitability reigns, each phase presents its unique challenges and requires tailored strategies for thriving in the ever-evolving business arena.
Existence Stage:

The existence stage is the initial phase of a small business, where the primary focus is establishing the company and ensuring its survival. At this point, the industry is just starting and may still need to generate substantial revenue.
Challenges: Small businesses in this stage often face the challenge of attracting their first customers, managing startup costs, and fine-tuning their products or services to meet market demand.
Strategies:
Securing initial funding or investment to cover startup expenses.
Developing a minimum viable product (MVP) to test the market.
Building a customer base through targeted marketing efforts.
Creating a solid business plan to guide future growth.
Survival Stage:
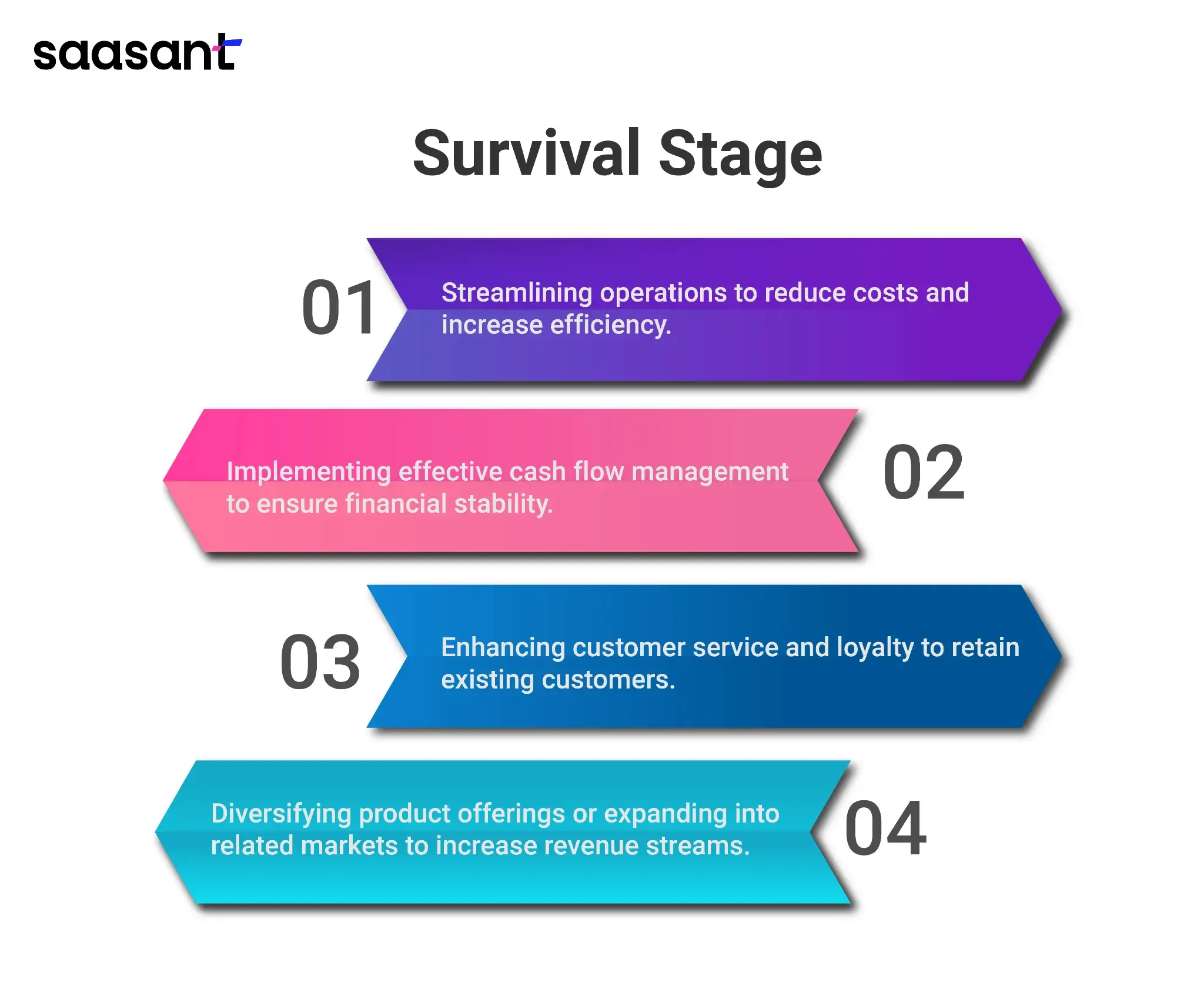
In the survival stage, the business has stabilized and is generating enough revenue to cover its ongoing expenses. The focus shifts from mere survival to achieving consistent profitability.
Challenges: Small businesses in this stage must continue to attract and retain customers, manage cash flow, and establish efficient operational procedures.
Strategies:
Streamlining operations to reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Implementing effective cash flow management to ensure financial stability.
Enhancing customer service and loyalty to retain existing customers.
Diversifying product offerings or expanding into related markets to increase revenue streams.
Take-off Stage:
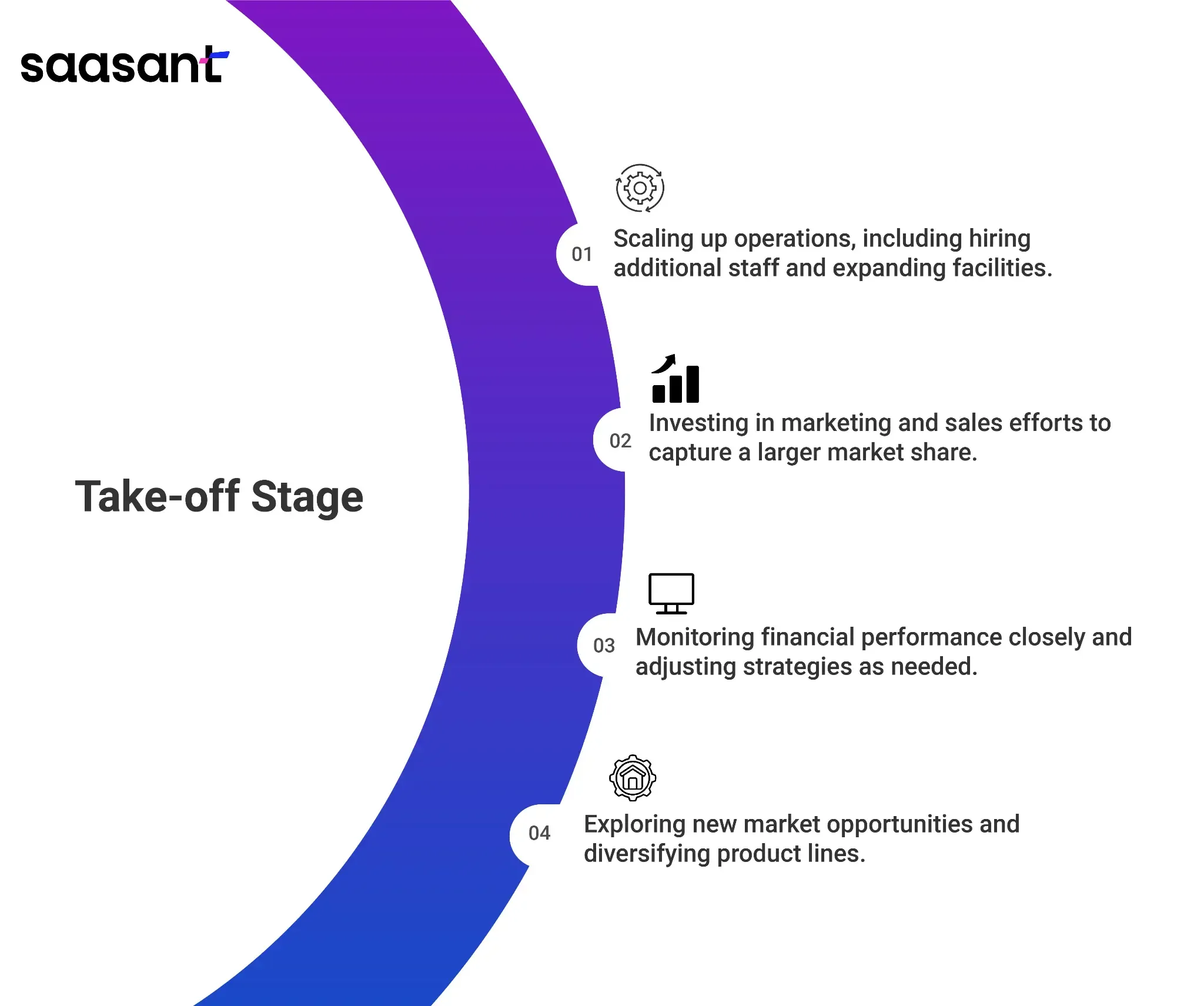
Rapid growth is the character of the take-off stage. The business gains momentum, expands its customer base, and experiences a surge in sales and revenue. This stage can be both exciting and challenging.
Challenges: Small businesses in the take-off stage must manage the complexities of rapid growth, maintain product quality and customer service, and secure additional resources to support expansion.
Strategies:
Scaling up operations, including hiring additional staff and expanding facilities.
Investing in marketing and sales efforts to capture a larger market share.
Monitor financial performance closely and adjust strategies as needed.
Exploring new market opportunities and diversifying product lines.
Success Stage:
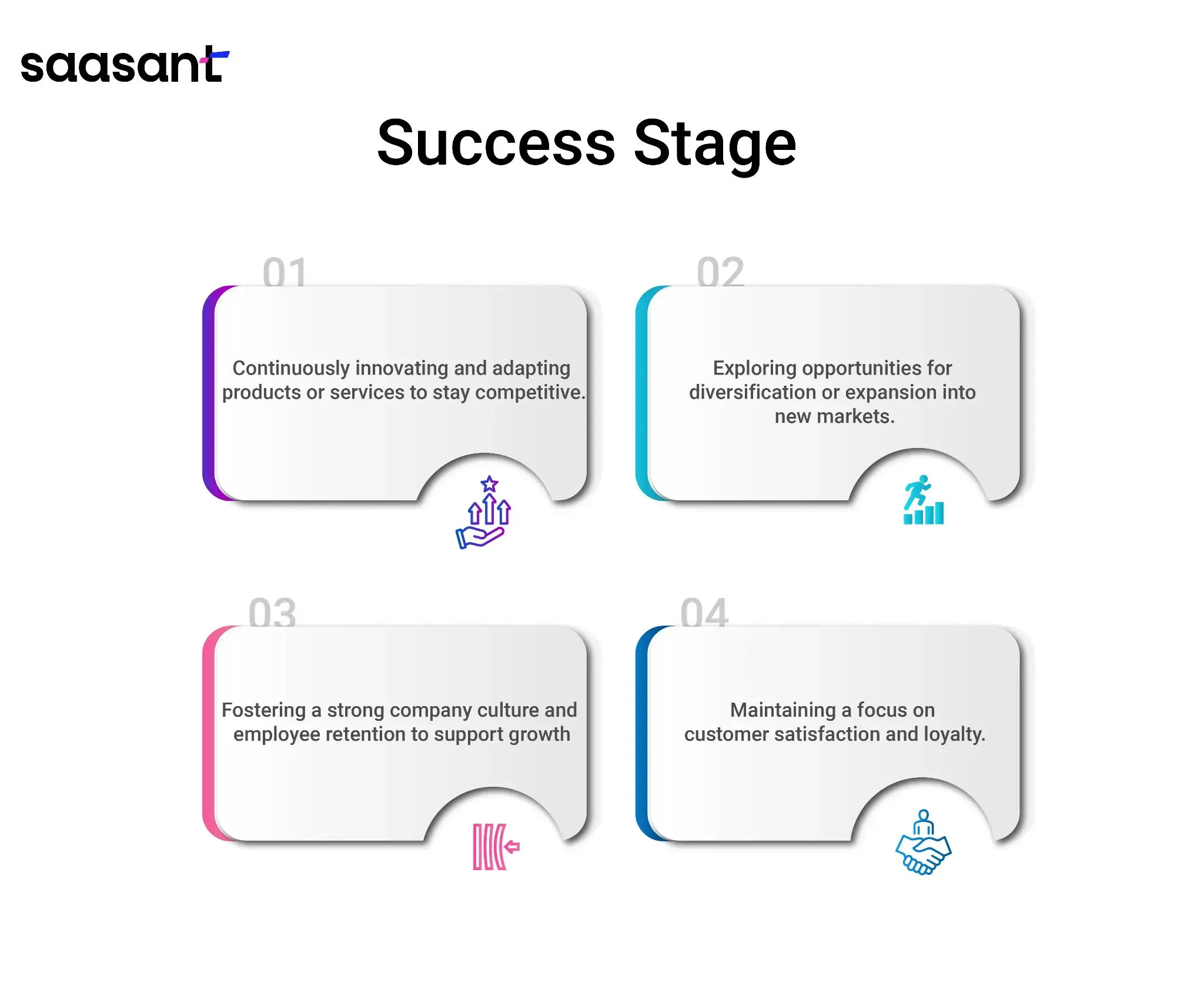
The success stage represents the pinnacle of small business growth. At this point, the business is well-established, profitable, and may have achieved a dominant position in its market. It has the option to consider further expansion or diversification.
Challenges: Small businesses in the success stage may face challenges in maintaining their market share, sustaining profitability, and adapting to changing market conditions.
Strategies:
Continuously innovate and adapt products or services to stay competitive.
Exploring opportunities for diversification or expansion into new markets.
Fostering a strong company culture and employee retention to support growth.
Maintaining a focus on customer satisfaction and loyalty.
10 Success Strategies for Small Businesses
Success hinges on a carefully crafted set of strategies. It starts from fostering customer loyalty through personalized programs to harnessing the power of cost-effective digital marketing; small businesses navigate these difficult terrains with determination. Here are ten successful strategies that could serve as a beacon light for entrepreneurs striving to make a mark in the business world.
Customer Loyalty Programs:
Customer loyalty programs are designed to reward and retain existing customers. These programs often provide incentives such as discounts, exclusive offers, or loyalty points for repeat purchases. Small businesses can encourage customers to return by implementing a well-structured loyalty program, increasing their lifetime value and profitability.
Networking Events:
Attending industry-specific networking events provides small businesses valuable opportunities to build relationships and expand their business network. These events can include conferences, trade shows, seminars, and local business gatherings. Networking allows businesses to connect with potential customers, partners, suppliers, and industry peers, fostering collaborations and opening doors to new opportunities.
Effective Marketing Efforts:
Small businesses often operate with limited budgets, so focusing on cost-effective digital marketing strategies is crucial. It may include social media marketing, content marketing, email marketing, and search engine optimization (SEO). Effective digital marketing enables businesses to reach a wider audience and engage with potential customers without the high costs associated with traditional advertising.
Strategic Planning:
A clear business strategy is essential for guiding a small business toward success. This strategy should include well-defined objectives, target markets, competition analysis, and financial projections. Moreover, it should adapt to market and business environment changes. Regularly reviewing and adjusting the strategy ensures the business remains aligned with its goals.
Customer Engagement:
Building a loyal customer base requires consistent and meaningful customer engagement. Small businesses should actively interact with customers through various channels, including social media, email, and in-person interactions. Personalized communication, addressing customer feedback, and providing exceptional customer service can enhance engagement and loyalty.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR):
Embracing CSR initiatives demonstrates a business's commitment to social and environmental values. Small businesses can support causes that align with their mission, whether donating a portion of profits to charity, reducing their carbon footprint, or engaging in community outreach programs. CSR benefits society, enhances the business's reputation, and appeals to socially conscious consumers.
Resource Management:
As a small business grows, effective resource management becomes increasingly important. Allocating resources involves hiring and training employees, improving operational procedures, and optimizing inventory management. Efficient resource allocation allows the business to meet growing demands without unnecessary expenses or inefficiencies.
Market Expansion:
Exploring new markets and growth opportunities can be a game-changer for small businesses. Diversifying customer segments or geographic locations can reduce dependence on a single market and enhance market share. Conducting thorough market research and understanding different markets' unique needs and preferences is essential to successful business expansion.
Collaborating with Co-founders:
Small business owners can benefit from collaborating with co-founders with complementary skills, expertise, and resources. A co-founder can share the workload, contribute additional capital, and offer diverse perspectives. A well-aligned partnership can help navigate challenges and seize opportunities more effectively.
Sustainability and Cost Efficiency:
Offering sustainable products or services and adopting cost-effective practices can improve a small business's bottom line. Sustainable practices appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and can reduce operating costs in the long run. Implementing lean processes, optimizing supply chains, and continuously seeking ways to cut unnecessary expenses contribute to cost efficiency.
Conclusion
Small businesses are the backbone of economies worldwide, and their growth is essential for economic prosperity. While they face unique challenges, small business owners can navigate these obstacles and succeed by implementing the right strategies at each growth stage. Small businesses can achieve long-term success by prioritizing customer loyalty, strategic planning, and corporate social responsibility.
Frequently Asked Questions
What defines a small business?
Small businesses, which account for over 99% of all companies in the United States, typically have fewer than 500 employees and generate less than $7.5 million in annual revenue. Despite their modest scale, they drive innovation and create about two-thirds of new jobs annually. These enterprises are crucial for economic vitality, representing a significant portion of GDP and fostering entrepreneurship nationwide.
What are the key challenges that small businesses face?
As small businesses operate, they often encounter challenges such as limited resources, acquiring new customers, retaining existing customers, developing effective marketing strategies, and practicing corporate social responsibility with tight budgets.
What are the stages of small business growth?
Small businesses typically go through the existence stage (formation), survival stage (stabilization), take-off stage (rapid growth), and success stage (well-established and profitable) as they grow and evolve. Understanding these stages is crucial for strategic planning.
What are some success strategies for small businesses?
Success strategies for small businesses include implementing customer loyalty programs, attending networking events, focusing on cost-effective marketing, strategic planning, customer engagement, corporate social responsibility, resource management, market expansion, collaborating with co-founders, and adopting sustainability and cost-efficient practices. These strategies help small businesses navigate their unique challenges and achieve growth.
How can small businesses increase their sales and revenue?
Small businesses can boost sales and revenue by implementing effective marketing strategies to reach a broader audience, offering promotions or discounts to attract new customers, upselling and cross-selling to existing customers, and continuously improving their products or services to meet customer needs and preferences.
What role do networking events play in small business growth?
Networking events provide valuable opportunities for small businesses to build relationships, establish partnerships, and expand their professional network. These events can lead to new business collaborations, customer referrals, and access to valuable resources.
How can small businesses maintain customer loyalty and retention?
Small businesses can maintain customer loyalty by providing exceptional customer service, implementing loyalty programs, regularly engaging with customers through personalized communication, and promptly addressing customer feedback and concerns.
What is the significance of corporate social responsibility (CSR) for small businesses?
Corporate social responsibility allows small businesses to demonstrate their commitment to social and environmental values. Engaging in CSR initiatives benefits the community, enhances the business's reputation, and appeals to socially conscious consumers, potentially increasing customer loyalty.
What marketing strategies can small businesses employ on a tight budget?
Small businesses on tight budgets can utilize cost-effective marketing strategies such as content marketing, social media engagement, and email marketing. These methods allow companies to reach their target audience without significant advertising expenses.
How can small businesses effectively manage their resources as they grow?
Small businesses can manage their resources effectively by optimizing operational procedures, investing in employee training and development, and continuously evaluating resource allocation to meet growing demands without unnecessary expenses or inefficiencies.