Cash, Accrual, and Hybrid Accounting: Choosing the Right Method for Your Business

When managing your business's finances, choosing the suitable accounting method is one of the most critical decisions. Two of the most common approaches are cash and accrual accounting, each with advantages and considerations. In recent years, a hybrid accounting method has also gained popularity. In this blog post, let us explore what cash and accrual accounting entails, discuss the pros and cons of each, and introduce you to the hybrid accounting method to help you make an informed decision for your business.
Contents
Understanding Cash Accounting
1. Revenue Recognition:
2. Expense Recognition:
3. Simplicity:
4. Tax Advantages:
Understanding Accrual Accounting
1. Revenue Recognition:
2. Expense Recognition:
3. Accuracy:
4. Compliance:
Example: Profit & Loss Report Prepared Under Both Methodologies
Cash Accounting Methodology
Accrual Accounting Methodology
Comparison and Implications
Pros and Cons of Cash vs. Accrual Accounting
Cash Accounting Pros:
Cash Accounting Cons:
Accrual Accounting Pros:
Accrual Accounting Cons:
Introducing Hybrid Accounting
Tax Implications of Cash Accounting
The Challenges of Hybrid Accounting:
Choosing the Right Accounting Method for Your Business
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding Cash Accounting
Cash accounting, also known as the cash basis of accounting, is a straightforward method that records financial transactions when money changes hands. Here are the key features of cash accounting:
1. Revenue Recognition:
Under cash accounting, payment, when received from customers, is revenue. You report income when your bank account gets a cash deposit and when you receive it.
2. Expense Recognition:
Payments made to suppliers, employees, or other parties are considered expenses. In cash accounting, you don't consider accounts payable or accounts receivable.
3. Simplicity:
Cash accounting is relatively simple and suitable for small businesses with straightforward financial transactions. It provides a clear picture of your cash flow.
4. Tax Advantages:
Some businesses prefer cash accounting for tax purposes because it allows them to delay paying taxes on revenue until it's received.
Understanding Accrual Accounting
Accrual accounting, on the other hand, is a more complex method that records financial transactions when they occur, regardless of when the actual cash changes hands. Here's what you need to know about accrual accounting:
1. Revenue Recognition:
The company recognizes revenue when it earns it before receiving payment. This approach aligns income with the expenses it incurs.
2. Expense Recognition:
The company records expenses when it incurs them, not necessarily when paid. This process encompasses accounts payable and accounts receivable.
3. Accuracy:
Accrual accounting provides a more accurate picture of your business's financial health, especially for larger or more complex businesses.
4. Compliance:
Publicly traded companies, businesses with high revenue thresholds, or businesses entering into agreements with lenders or investors are required by law or accounting standards to use accrual accounting.
Example: Profit & Loss Report Prepared Under Both Methodologies
John runs a small landscaping business and uses two accounting methodologies to prepare his Profit & Loss Report. Using a different scenario, let's examine how cash and accrual accounting impact his finances.
Cash Accounting Methodology
In this scenario, John runs his business using cash accounting, where the system records transactions only during cash exchange. Here's a breakdown of his financial activities for September:
On September 1st, John purchased gardening equipment for $1,000, which he paid for immediately. Throughout September, John provided landscaping services to various clients, totaling $2,500. However, he only received $1,800 in cash payments from clients during the same month. On September 10th, John paid $500 for maintenance and repairs on his equipment.
Under cash accounting, John's Profit & Loss Report for September would look like this:
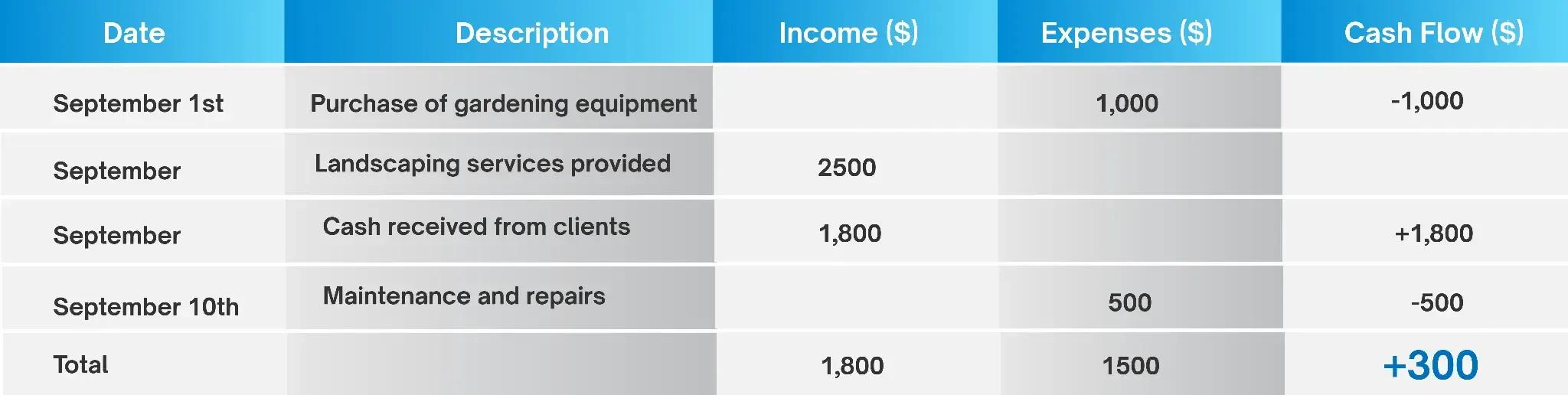
In this scenario, John reports a net profit of $300 for September because he only accounts for cash transactions during the month.
Accrual Accounting Methodology
Let’s examine financial activities prepared using the accrual accounting methodology. Accrual accounting recognizes revenue when earned and expenses when incurred, regardless of when the cash exchange occurs.
Under accrual accounting, John's Profit & Loss Report for September would look like this:
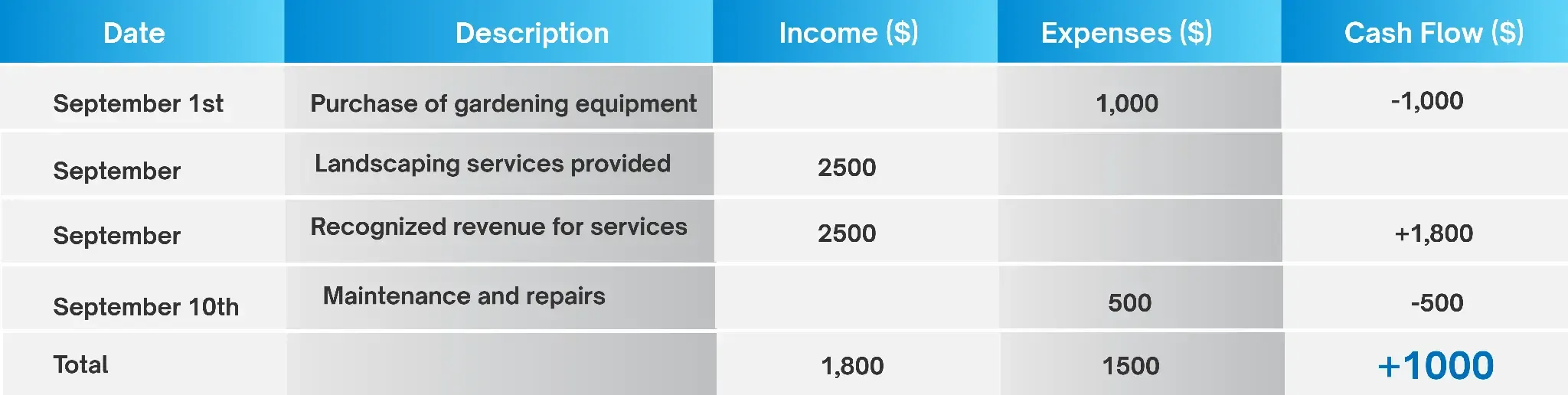
In this scenario, John reports a net profit of $1,000 for September because he recognizes revenue when he provides services, even if he has not received full payment from all clients during the month.
Comparison and Implications
John's cash accounting shows a profit of $300 for September, while accrual accounting shows a profit of $1,000. The difference arises from recognizing revenue when earned (accrual) versus when cash is received (cash accounting).
Accrual accounting provides a more accurate representation of John's financial situation by matching revenue with related expenses. This method better reflects the business's financial health and aids in making informed decisions about future investments, costs, and growth strategies.
While cash accounting can be more straightforward and used mainly by small businesses, John might opt for accrual accounting when seeking loans or making long-term financial decisions, as it offers a more comprehensive view of his business's financial performance.
Pros and Cons of Cash vs. Accrual Accounting
Now that you understand the basics of both cash and accrual accounting, let's weigh the pros and cons of each:
Cash Accounting Pros:
Simplicity: It's easy to understand and implement, making it ideal for small businesses.
Realistic cash flow view: It reflects the actual money you have on hand.
Tax benefits: You can delay paying taxes on revenue until you receive payments.
Cash Accounting Cons:
Limited insight: It may not provide an accurate financial picture, especially for businesses with long sales cycles or substantial accounts payable/receivable.
Compliance issues: Companies with complex transactions or businesses seeking external funding may not be allowed to use cash accounting due to regulatory requirements.
Accrual Accounting Pros:
Accuracy: It offers a more accurate financial snapshot, especially for larger or more complex businesses.
Better long-term planning: It helps businesses plan for future expenses and revenue by recording transactions when they occur.
Compliance: Financial Services, healthcare firms with insurance billing, and real estate companies with long-term projects must use accrual accounting.
Accrual Accounting Cons:
Complexity: Implementing and understanding can be more challenging, especially for small businesses.
Tax implications: Businesses using accrual accounting may need to pay corporate income taxes on income before receiving the cash.
Introducing Hybrid Accounting
Hybrid accounting is a relatively new approach combining cash and accrual accounting elements. It aims to provide a more flexible way to manage finances. Here's how it works:
Revenue Recognition: Businesses using the hybrid method can choose to recognize revenue on a cash or accrual basis. If a business is primarily concerned with managing cash flow and prefers to align revenue recognition with actual cash receipts, it may choose to recognize revenue on a cash basis. Businesses that prioritize accurate financial reporting and want to match revenue with the economic activities that generate it may opt for an accrual basis.
Expense Recognition: Similar to revenue, businesses can select whether to recognize expenses when paid (cash basis) or when they are incurred (accrual basis).
Flexibility: Hybrid accounting allows businesses to switch between cash and accrual accounting methods based on their financial goals, size, or regulatory requirements.
Real-Time Reporting: It provides the option for real-time financial reporting, which can benefit decision-making.
Tax Implications of Cash Accounting
In Cash Accounting, businesses can only claim expenses within the same tax year, typically from January to December. For example, if a company incurs expenses in December 2024 but pays them in 2025, they can only deduct them in their 2025 tax return. Similarly, if a company provides a service in 2024 but receives payment in 2025, the revenue is reported in the 2025 tax return rather than the 2024 return.
Some businesses view this as an advantage of Cash Accounting since it allows for deferral of VAT payments on income that has yet to be received. However, it's essential to note that this tax deferral is temporary, and payments even out over the years. While businesses can switch between Cash and Accrual Accounting each year, doing so can add administrative complexity. Strict rules ensure income and expenses are only reported once in the tax return.
The Challenges of Hybrid Accounting:
The Hybrid Accounting method combines Cash and Accrual Accounting elements, offering flexibility for certain businesses. However, this approach requires adherence to specific IRS norms like consistency in accounting method from year to year and filing of IRS Form 3115 (requesting a change in the accounting method).
Hybrid Accounting can be challenging for those without extensive accounting knowledge, so consulting with a professional accountant is recommended to assess its suitability and tax implications. Special rules apply when using the hybrid model, such as matching the accounting method for reporting income with the method used for reporting expenses. Additionally, businesses with inventory must use the accrual accounting method to record sales and purchases.
Choosing the Right Accounting Method for Your Business
Business Size:
Small Businesses: Cash accounting is often a good choice for startups and small businesses with straightforward financial transactions. It simplifies bookkeeping and aligns with the cash flow nature of small enterprises.
Larger Businesses: Accrual accounting is generally more suitable for larger businesses with complex financial operations. It provides a more comprehensive view of financial performance, which is beneficial for managing large-scale companies.
Regulatory Requirements:
Some industries or jurisdictions may require businesses to use a specific accounting method. It's crucial to be aware of any legal or regulatory obligations related to accounting in your industry.
Financial Goals:
Consider your financial goals and whether you need the accuracy of accrual accounting for long-term planning. Accrual accounting provides a clearer financial picture if you want to secure investments, apply for loans, or plan for future growth.
Tax Implications:
Evaluate the tax implications of each accounting method. In some regions, businesses below a certain revenue threshold may have the option to choose between cash and accrual accounting for tax purposes. Consult with a tax professional to understand how each method affects your tax liability.
Flexibility Needs:
If you want the flexibility to switch between accounting methods based on changing circumstances, hybrid accounting may be a viable option. Hybrid accounting allows you to use cash accounting for one aspect of your business and accrual accounting for another, providing a tailored approach.
Reporting and Decision-Making:
Consider how you'll use financial reports to make decisions and whether real-time reporting is essential. Accrual accounting provides a more accurate reflection of your business's financial health over time, enabling better-informed decisions. Cash accounting may need to capture long-term financial trends more effectively.
Conclusion
Choosing the suitable accounting method for your business involves carefully considering factors such as size, regulatory requirements, financial goals, and reporting needs. While cash accounting is more straightforward and offers tax advantages, accrual accounting provides a more accurate financial picture. The hybrid accounting method allows for flexibility and can be a valuable option for businesses looking to adapt to changing circumstances.
Ultimately, consulting with a financial advisor or accountant can help you make an informed decision that aligns with your business's needs and goals. Remember that your chosen accounting method will significantly impact your financial reporting and decision-making, so choose wisely. When you're ready to simplify your accounting and seamlessly sync your e-commerce data with QuickBooks or Xero, consider using PayTraQer. Automate syncing of e-commerce data, reconcile payments accurately and customize settings to match your workflow preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cash accounting?
Cash accounting is an accounting method that records financial transactions when actual cash changes hands. It recognizes revenue when payment is received and expenses when paid.
What is accrual accounting?
Accrual accounting is an accounting method that records financial transactions when they occur, regardless of the cash exchange timeline. It recognizes revenue when earned and expenses when incurred.
What is hybrid accounting?
Hybrid accounting is an approach that combines elements of both cash and accrual accounting. It offers flexibility in choosing when to recognize revenue and expenses and allows for real-time reporting.
Why would a small business choose cash accounting?
Small businesses often choose cash accounting for its simplicity and tax benefits. It provides a clear view of actual cash flow and allows for delayed tax payments on revenue.
Why might a large business prefer accrual accounting?
Large businesses often prefer accrual accounting for its accuracy, especially when dealing with complex financial operations. It offers a more comprehensive financial picture, reflecting all economic activities, which can be particularly useful for understanding long-term financial trends and making informed decisions.
What are the tax implications of cash accounting?
Cash accounting can delay tax payments on revenue until cash is received, providing potential tax advantages for businesses.
Are there industries that are required to use accrual accounting?
Yes, some industries or businesses, especially those publicly traded or with significant revenue, may be required by law or accounting standards to use accrual accounting.
What is the benefit of hybrid accounting's flexibility?
Hybrid accounting allows businesses to switch between cash and accrual methods based on changing circumstances or regulatory requirements, offering adaptability in financial management.
How does hybrid accounting impact reporting and decision-making?
Hybrid accounting provides the option for real-time reporting, which can aid businesses in making timely and informed financial decisions.
How can I determine the suitable accounting method for my business?
Consider factors such as the size of your business, regulatory requirements, financial goals, tax implications, flexibility needs, and reporting preferences. Consulting with a financial advisor or accountant can also help you make an informed decision tailored to your needs.