What is Bookkeeping? - Ultimate Guide

Let’s be honest! No one starts a business to do bookkeeping. But just because bookkeeping might look mundane, it can’t be ignored! From tax prep and compliance with regulations to making informed business decisions, bookkeeping keeps your business alive and thriving.
What was seen as a tedious task in the past has become appealing due to the rise of bookkeeping automation. Small businesses in the US trying to up their bookkeeping game should read this piece. Let us cover the fundamentals of bookkeeping, learn about basic QuickBooks account setup, and tap into e-commerce bookkeeping for a holistic understanding of small business bookkeeping.
“Making good judgments when one has complete data, facts, and knowledge is not leadership - it's bookkeeping,” said Dee Hock, founder and CEO of the Visa credit card association.
Contents
What is Bookkeeping?
Why is Bookkeeping Important?
How does Bookkeeping work?
Getting Started with Bookkeeping: The Beginner’s Blueprint
What is E-commerce Bookkeeping?
Conclusion
FAQs
What is Bookkeeping?
Bookkeeping regularly records and classifies a company’s financial transactions into organized accounts. With proper bookkeeping, companies can track the information on their books to make key investing, operating, and financing decisions.
Don’t ever conclude that bookkeeping is just numbers on a spreadsheet; it is an art that requires skill, creativity, and judgment in equal proportion. Accounting is often confused with bookkeeping, but these two terms are different.
Bookkeeping vs Accounting: What’s the Difference?
Bookkeeping involves collecting and arranging financial information, encompassing responsibilities like creating invoices, managing bills, processing payroll, and ensuring transactions match up. On the other hand, accounting involves understanding and communicating this financial data, which includes preparing tax returns, conducting audits, and analyzing financial performance.
Every business must establish a bookkeeping and accounting system to compile financial records at the end of each year or quarter. These processes help the company assess its value and make informed decisions for future success.
A natural question might arise for businesses starting afresh: do small businesses need to do bookkeeping?
Yes! Here is a quick answer for you.
What Happens If You Don’t Do Bookkeeping?
Paying attention to bookkeeping can lead to a backlog of financial tasks, obscure financial visibility, and result in cash flow problems. Inaccurate financial records may lead to overpaying taxes and cause difficulties during audits. A financial audit is a systematic examination and verification of a company's financial records, transactions, and statements by an independent and qualified professional, known as an auditor, to assess the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of the financial information presented.
Why is Bookkeeping Important?
Bookkeeping is crucial for businesses because it provides essential financial insights, enables effective financial planning, ensures compliance with tax regulations, and enhances stakeholder transparency. It is the foundation for financial success and growth by accurately recording and organizing financial data.
Budgeting: Bookkeeping is crucial as it helps businesses plan, control expenses, identify spending trends, and prepare for emergencies by tracking income and expenses accurately.
Tax Preparation: Proper bookkeeping ensures tax compliance, maximizes deductions and credits, and reduces stress during tax season by maintaining organized financial records.
Financial Information: Bookkeeping provides essential data for informed decision-making, builds investor confidence through transparency, and fosters trust among stakeholders by offering a clear view of the company's financial health.
How does Bookkeeping work?
Bookkeeping starts with transactions recorded using source documents like receipts, invoices, and payables. These documents provide the information needed to track and organize financial activities accurately.
Most businesses find it challenging to maintain every receipt, and that’s why their monthly bank statements could be an accurate alternative. The next big thing is the financial effects of transactions.
What are the Financial Effects of Your Transactions?
Expert bookkeeping guidance is needed to understand the complete financial effects of your transaction. However, as a small business, you can learn the fundamental effects of your financial transactions right here. All your business transactions fall into one of these five categories.
Revenue: Revenue is what you make from selling your products and services (sales)
Expenses: Expenses are costs incurred associated with running your business (Advertising, office rent)
Assets: Assets are resources owned by the company with a measurable future value (inventory and prepaid expenses)
Liabilities: Liabilities are what the companies owe to creditors (loans and credit cards)
Equity: Equity is the degree of ownership in your business (distribution and contribution)
Classifying your business transactions is vital so a company can accurately interpret its financial performance. Now, you’ll clearly understand what bookkeeping is and how the cycle of bookkeeping works. Let’s get started with actual bookkeeping!
Getting Started with Bookkeeping: The Beginner’s Blueprint
You might wonder how to begin with all these bookkeeping basics as a business owner. Worry not! Here is a simple five-step process to get you started with bookkeeping.
#1 The Importance of Having a Separate Business Account
The first step in your bookkeeping journey - opening a business bank account. You’re not legally required to do this as a sole proprietor. But have a separate business bank account to keep your books clean and straightforward. Also, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) expects businesses like LLCs and CCorps to have a separate business bank account.
If the IRS comes to know they don’t have a separate account, it means the termination of those businesses by IRS standards. Furthermore, consider the ease of organizing books during tax time. Instead of rummaging through a year of deposits and expenses and trying to remember what was personal and business, centralize everything in your business bank account.
Most banks offer a business bank account option, and you just want to ensure you have an Employee Identification Number (EIN). You can request this 9-digit EIN from the IRS. Use Form SS-4 to apply for the Employer Identification Number (EIN).
#2 Setting up a Bookkeeping System
Bookkeeping is an ongoing process for every business. This process should be completed monthly to stay on top of your finances. Before we know how to establish a bookkeeping system, let us understand the importance of choosing a bookkeeping entry system.
Single-Entry Bookkeeping System: Single-entry bookkeeping is a straightforward approach to record-keeping where each transaction is documented once in a journal. This method focuses on cash transactions, monitoring cash flow in and out of the business.
Double-Entry Bookkeeping System: Double-entry bookkeeping is a system for logging financial transactions. Each business transaction results in entries made in at least two accounts, either as a debit or a credit. In this method, the total debits must always match the total credits, ensuring the books remain balanced.
Of these two, the double-entry bookkeeping system is the best way to record your transactions to have a complete picture of your finances. It also protects you from manual data entry errors.
Manual Bookkeeping vs. Automation Bookkeeping
Even in the modern era of the 21st century, it is still possible to manage your bookkeeping using traditional paper spreadsheets or physical account books. If manual accounting suits your requirements, switching to digital methods is unnecessary.
However, as your business expands, the volume of transactions you record will also increase. Manual bookkeeping can become time-consuming and raise the risk of significant errors. While it's relatively easy to double-check a dozen weekly entries for accuracy, doing the same for a thousand entries becomes impractical.
Essential computerized bookkeeping software can help recover some of the time lost to manual methods. Automated accounting programs offer even more significant time-saving benefits and additional advantages.
The Rise of Automated Bookkeeping Software
Applications such as Excel have been widely employed to streamline and improve various tasks. However, automation can handle repetitive tasks, transferring data from excel to accounting software, detecting inconsistencies and omissions, and minimizing the need for manual data entry.
The rise of automated bookkeeping software marks a significant shift in the accounting and financial management world. These advanced tools eliminate the tedium of manual data entry and offer real-time data analysis and robust reporting capabilities. Businesses that embrace this technology gain a competitive edge by managing their finances efficiently, making informed decisions, and staying compliant with ever-evolving financial regulations.
But how do you enjoy the benefits of bookkeeping automation? You have to invest in bookkeeping software like Xero or QuickBooks.
Investing in Bookkeeping Software
For example, if you’re picking QuickBooks as your go-to bookkeeping software, you can efficiently perform daily, weekly, and monthly bookkeeping tasks. You can connect your business bank account with the QuickBooks software to track income and expenses in an easy and less time-consuming way.
Additionally, setting up a bookkeeping system helps you classify your transactions in one of those five categories. But splitting the transactions as assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses, or revenue isn’t enough. You need to drill down further. For example, if you’re running a clothing store and you’re dumping your store with a substantial wholesale purchase of clothes, you need not label this as “inventory”; instead, you can give the label “summer inventory” or “winter inventory.”
Similarly, you might not name your online ad expenses as “online ads”; it is helpful for you to split those as “Facebook ads” or “Google ads.” Since it is easy for you to track how much you’re spending in each category. These types of scrutinizing are possible only if you know how to use bookkeeping programs like QuickBooks efficiently.
So, let's learn basic bookkeeping through QuickBooks so that you can enact some of the strategies discussed here in the real world. Make your business grow exponentially using the help of dedicated bookkeeping software.
Before setting up your account chart in QuickBooks, know a few more benefits of using a bookkeeping software.
Benefits of Bookkeeping Software for Your Business
Automated Data Import: Bookkeeping software can seamlessly connect with various financial sources, such as point-of-sale (POS) systems, invoicing software, and bank accounts. It automatically pulls transaction data from these sources, eliminating the need for manual data entry.
Transaction Reconciliation: The software speeds up the process of reconciling transactions. It matches incoming and outgoing payments with corresponding invoices or bills, ensuring that all financial records are accurate and balanced. This feature helps identify discrepancies or missing transactions.
Bill Payment Automation: It can automate the payment of bills and expenses. Once bills are entered into the system, the software can schedule payments based on due dates, ensuring that vendors and suppliers are paid on time. This feature helps avoid late fees and maintains good rapport with business partners.
Invoice Reminders: To improve cash flow, it can automatically send invoice reminders to customers who owe money. These reminders can be scheduled at predefined intervals or customized based on your payment terms. This proactive approach encourages timely payments and reduces outstanding accounts receivable.
Payment Status Tracking: Investing in a bookkeeping program keeps track of invoice payment statuses. It notifies you when customers have paid sales invoices. This real-time visibility into your receivables helps you monitor your cash flow and plan for future expenses or investments.
Setting Up a Basic Bookkeeping System Using QuickBooks
Let’s put your newfound knowledge into practice using QuickBooks. QuickBooks offers different subscription options. Choose the QuickBooks plan that suits your business needs.
Once you’re ready with a QuickBooks subscription, the next thing you need to do is set up your chart of accounts.
Setting up Chart of Accounts
Your chart of accounts is a complete list of your company’s accounts and balances. They are accounts or categories that you will place your transactions in. It is what a completed chart account looks like.
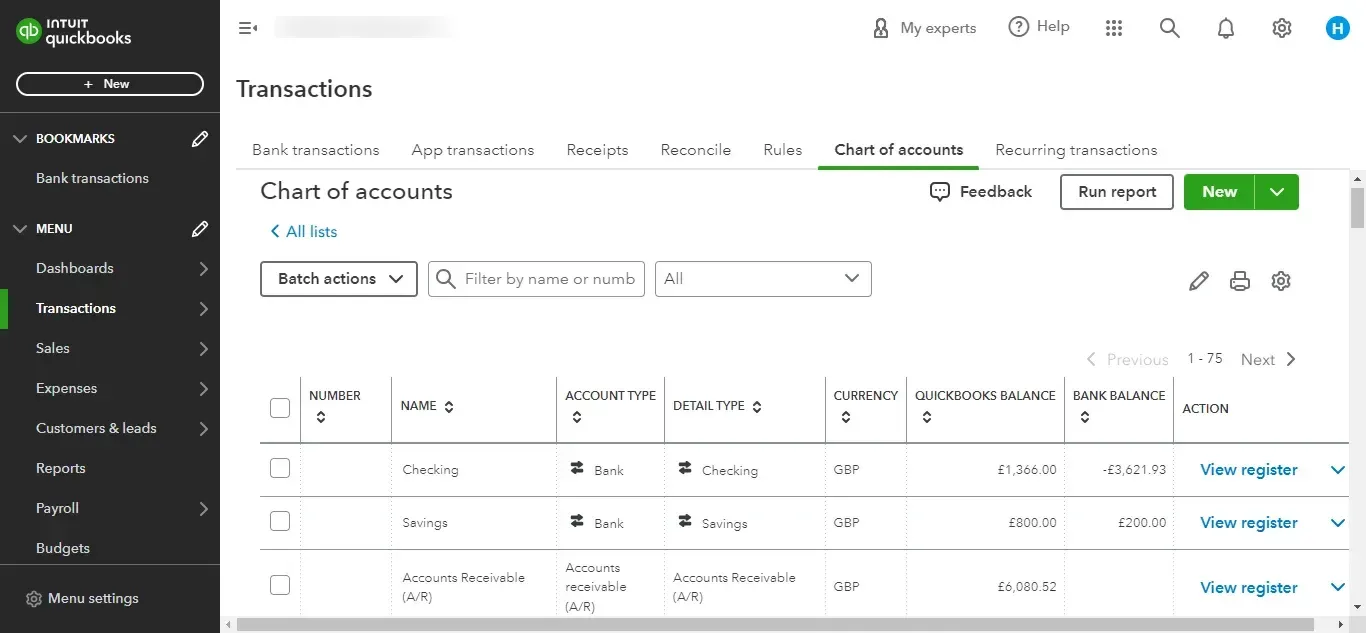
Each account has a name, type, detail type, and balance. All of these entities should be entered when setting up each account. Let us look at an example of setting up an account for “office rent.” You can keep track of your office lease payments if you follow these steps:
On the “Chart of Accounts” screen, click “New.”
Select “Expenses” as the account type from the drop-down.
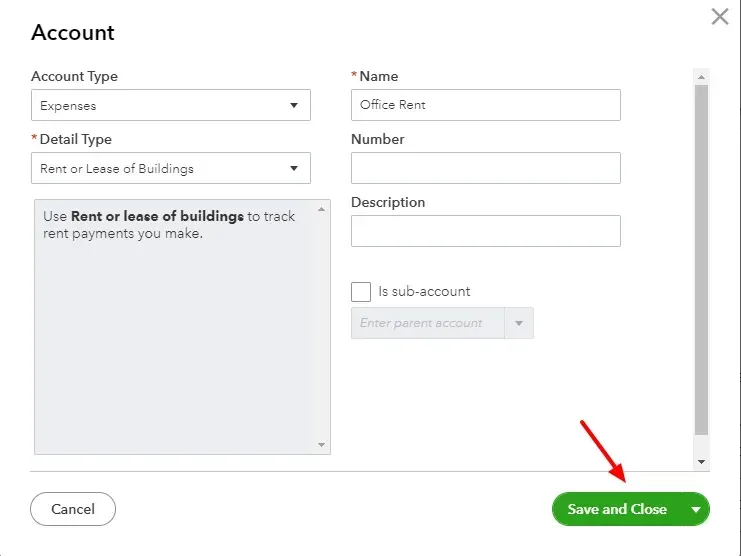
Choose the detail type “Rent or Lease of Buildings,” which is suitable. (Watch out for the description before you pick a detail type)
Next, in the Name field, type “Office Rent,” which is an appropriate name. This name will appear in your chart of accounts and financial statements.
Click on “Save and Close”. You’ll be redirected to the Chart of Accounts main page, where you can see the new account you created.
Note: Here are three things to consider while doing the above-mentioned steps.
Select the correct account type for each account. Assets should be assets, expenses should be expenses, and so on. When you improperly set up an expense for an asset, that account will show on the wrong financial statement.
To show sub-accounts for a few account types, check the “Is sub-account” box before clicking “Save and Close.” This sub-account will be displayed under the main account in the chart of accounts screen.
Create an account type for all kinds of business transactions. Avoid the easy work of classifying transactions as “miscellaneous” or “other.” It could cause difficulties in noticing valuable deductions during tax time. Customize the basic accounts list for the chart of accounts provided by QuickBooks to suit your business type. The less you categorize the transactions as “other” and “miscellaneous,” the more precise your chart of accounts will look.
Connecting Business Bank Account to QuickBooks
When you’re using a separate business bank account and connecting it to QuickBooks, your bank transactions will automatically show up in QuickBooks Online.
To connect your business bank account with QuickBooks Online, navigate to “Banking” in the main menu and select “Link account.” Read our detailed guide for further information on adding your bank account with QuickBooks, categorizing transactions, and setting up bank rules.
As you have your bank account and transactions connected to QuickBooks, it is time to classify your transactions.
Transactions Classification: Creating Sub-Categories
The chart of accounts you set up initially is back to work in this step. Select the appropriate vendor or customer name on each transaction's banking screen. If it is not there, create a new customer or vendor name.
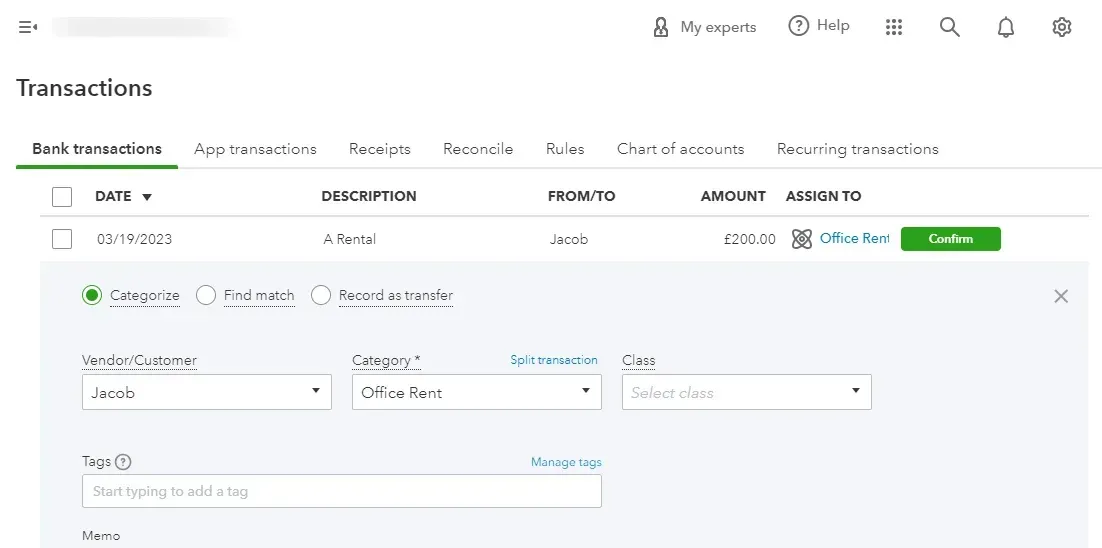
Choose the correct category; if the transaction is for office rent, select “office rent,” and if it is for sales, choose sales. Then, click on “Add”. Repeat this process for each transaction and each bank account. If you’re unsure about the category, choose “Ask Account” for categorizing a transaction type later.
Once you add a transaction, it gets included in your books and will appear on your company’s financial statements.
#3 Bank Reconciliation
Reconciling your transactions is determining any differences between the bank balance shown on your bank statement and your bookkeeping system. You want to ensure that all of your transactions are present and double-counted in your bookkeeping system.
It is good to perform bank reconciliation at least every month. It will help you catch errors or even billing mistakes your vendors make.
To do reconciliation in QuickBooks Online,
Click on “Chart of Accounts” and choose “Reconcile” from “Tools”. Now, choose which bank account you want to reconcile.
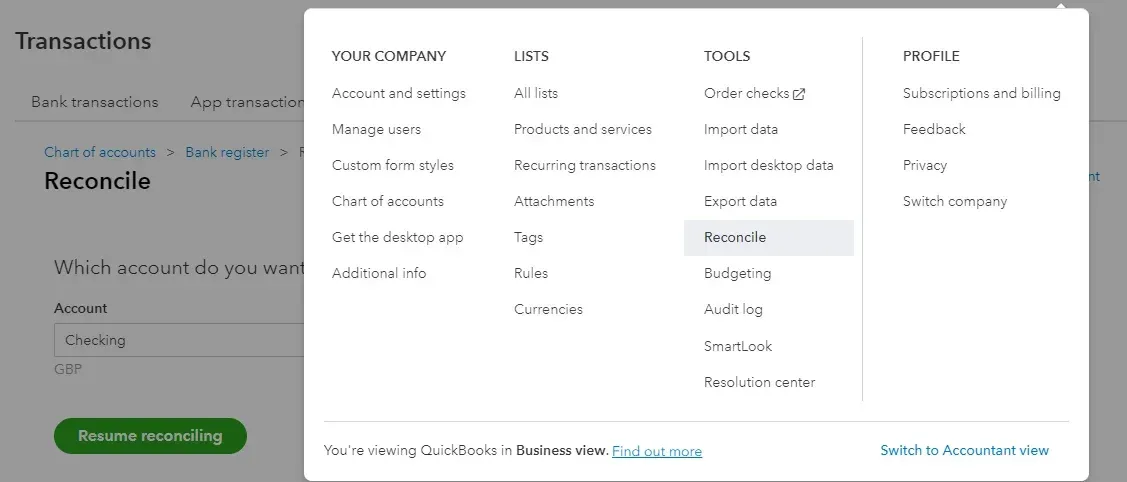
Now, check whether the beginning balance in your QuickBooks account is the same as the beginning balance in your bank statement.
Pick the ending balance value in the bank statement and enter it in the “Ending balance” box.
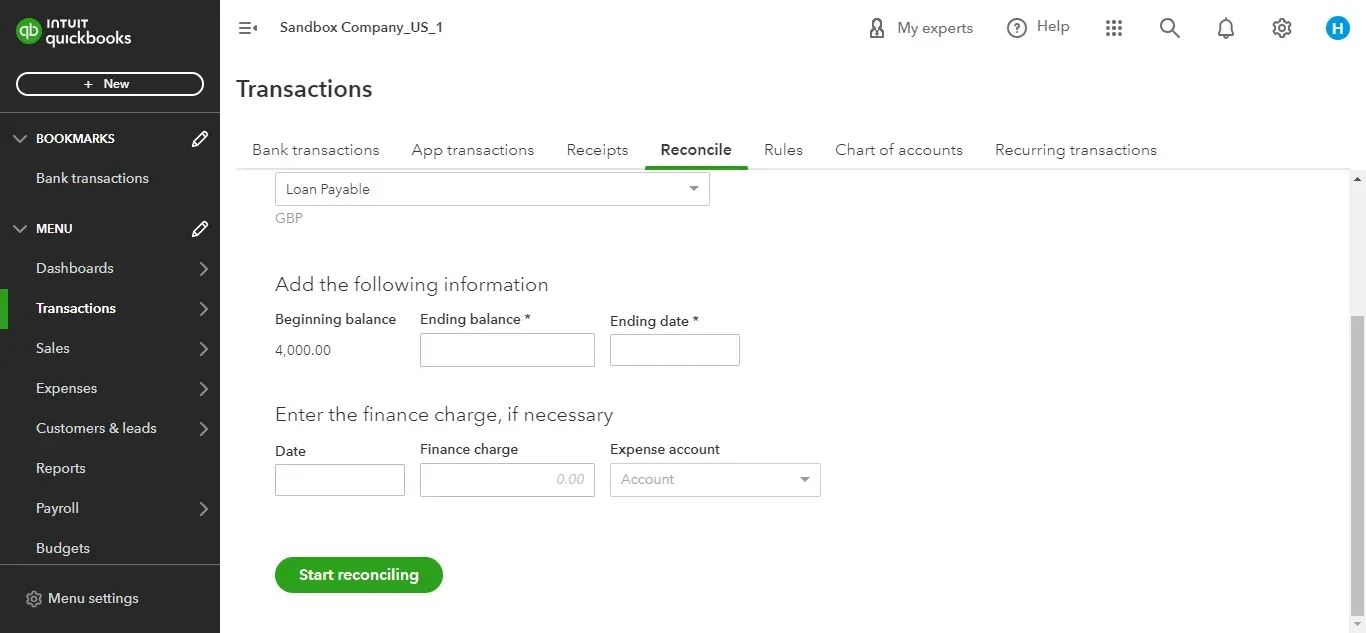
After you fill in the “Ending date,” you can start reconciling.
On the next screen, you can check every transaction in your bank statement.
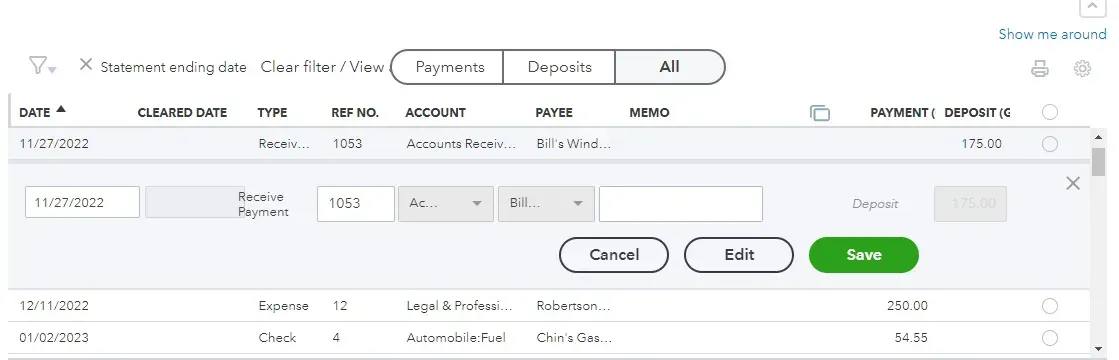
If the difference is zero, click “Finish now.”
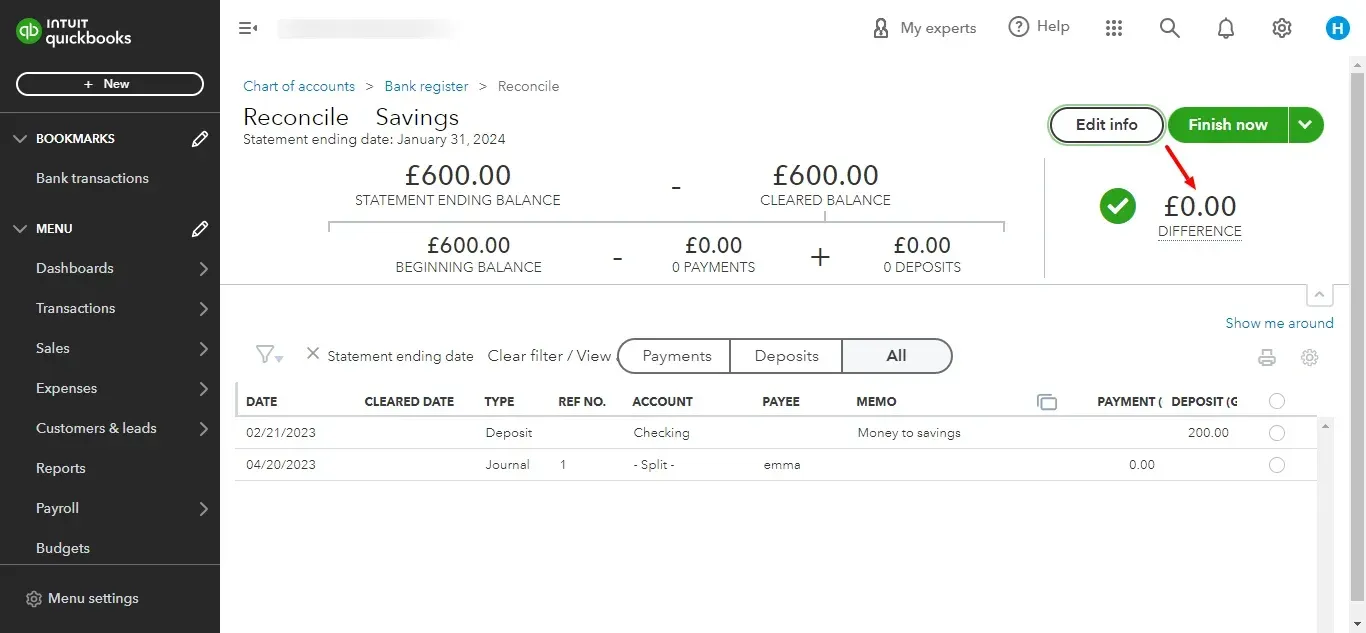
Look for errors in your transactions and make sure all your transactions are classified correctly. When you go through the transactions, the difference should be zero! If not, there might be an error with your beginning or ending balance. You could have mistakenly checked a transaction that was absent in the bank statement or missed a transaction in QuickBooks.
Remember, any transactions not matched to a bank statement transaction should be removed from your books to avoid misrepresenting your numbers. Likewise, any missing transactions should be added to your books.
#4 Prepare Financial Statements
Creating financial statements is a crucial and extensive responsibility that must be executed accurately to ensure the smooth operation of a business. These statements play a fundamental role in evaluating a company's financial well-being, facilitating informed decision-making, and pinpointing areas for potential growth and enhancement. Financial statements also provide businesses of all scales with essential insights to effectively manage expenses.
Balance Sheet: It shows your outstanding balance in assets, liabilities, and equities.
Income Statement (Profit & Loss): Your profit or loss for a specific period.
Cash Flow Statement: It explains the movement of cash related to your financing, investing, and operating activities.
Each of these reports should be prepared and reviewed at least monthly. Most of the work of preparing these statements is already done when your transactions are classified and reconciled.
How do you run reports for balance sheet statements in QuickBooks Online?
The balance sheet shows how much your company owes and owns!
Navigate to “Reports” in your QuickBooks Online menu and choose “Balance Sheet.”
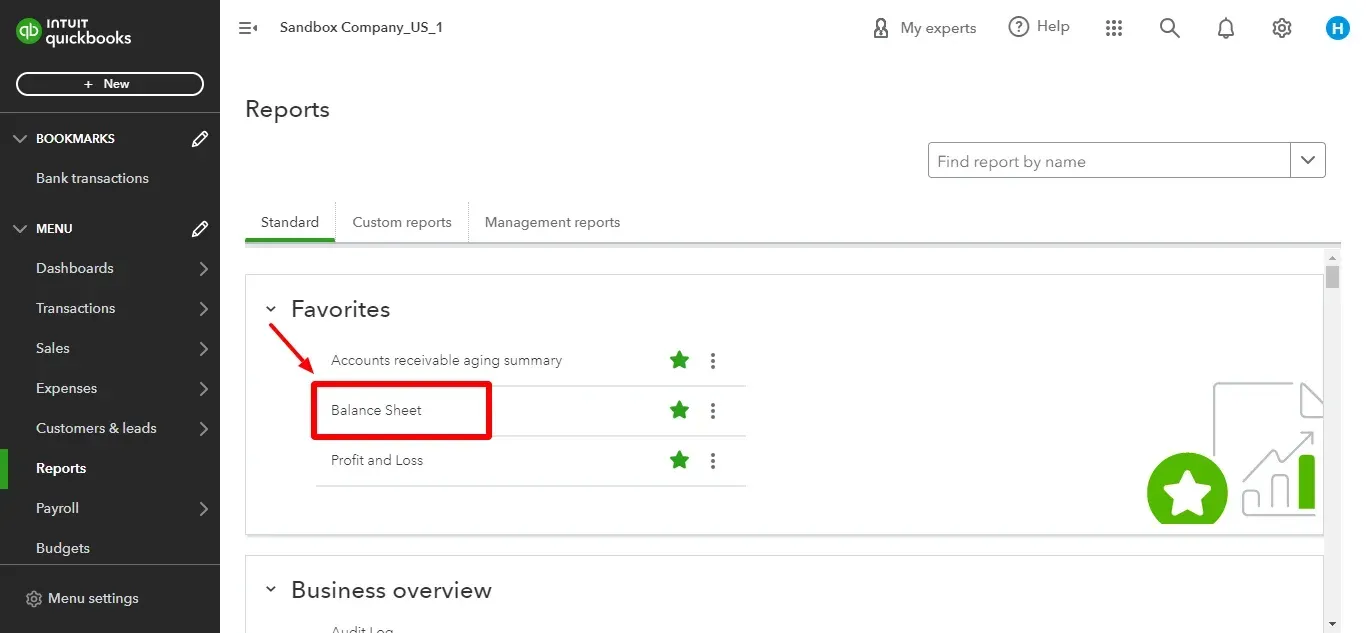
Customize the date according to your requirements and choose the accounting method (cash or accrual).
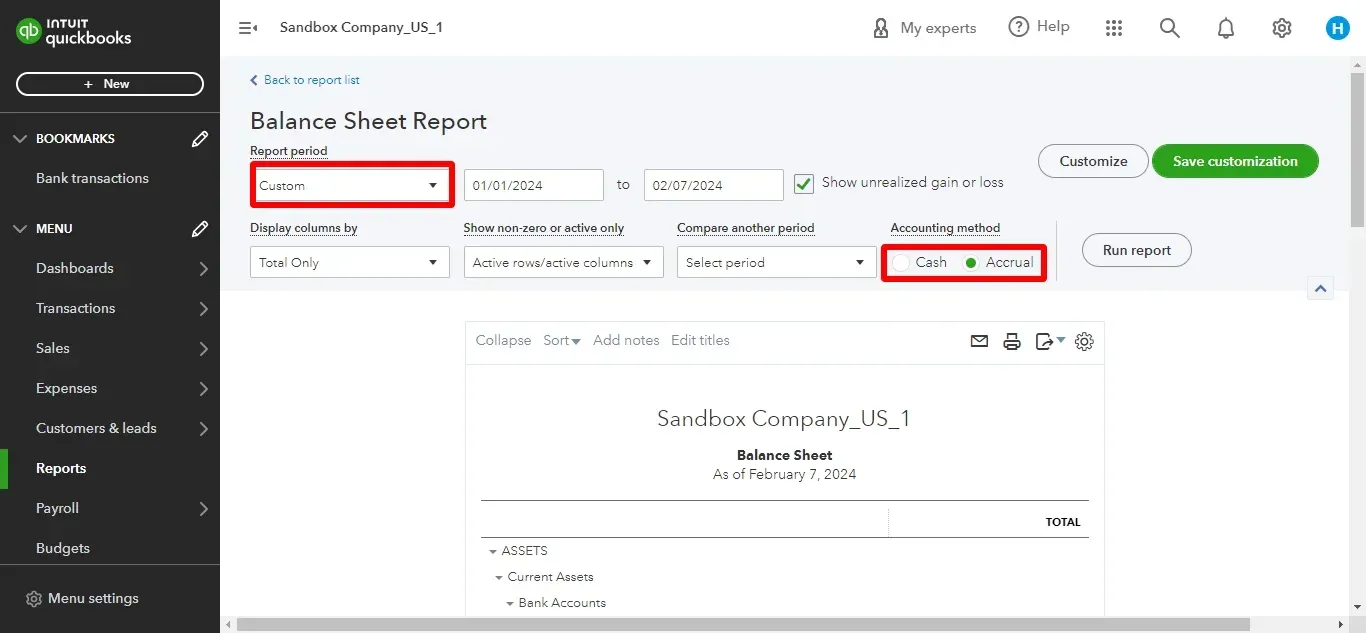
Hit “Run Report” to see your company’s assets, liabilities, and equity as of the report's ending date.
How to Run Reports for Profit & Loss Statement in QuickBooks Online?
The profit and loss statement shows how profitable your business is!
Navigate to “Reports” in your QuickBooks Online menu and choose “Profit & Loss.”
Customize the date according to your need, choose cash or accrual, and hit “Run Report.”

Here, you see your company’s income and expenses for a specific period.
If you’ve read and put some of the things discussed here into practice, you’d better understand what bookkeeping is and how to set up your bookkeeping in QuickBooks.
#5 Make Business Decisions from Your Books
Doing the above four steps boils down to one crucial aspect! Making better business decisions with the help of the financial information.
Effective business decision-making hinges on adeptly utilizing the insights gleaned from meticulous bookkeeping. The initial steps, including recording transactions, categorizing expenses, reconciling accounts, and generating financial statements, collectively contribute to a robust financial foundation. These organized and accurate records serve as a valuable resource for informed decision-making.
By scrutinizing financial data, businesses can assess profitability, identify cost-saving opportunities, and strategize for growth. Whether it's evaluating investment options, setting budgets, or optimizing operational efficiency, the ability to make well-informed decisions from comprehensive bookkeeping empowers businesses to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and steer toward sustained success.
Let's drill down a bit further and prefix e-commerce with bookkeeping. Though it looks the same on paper, e-commerce bookkeeping is trickier than regular bookkeeping. E-commerce bookkeeping is the first step toward e-commerce accounting.
What is E-commerce Bookkeeping?
E-commerce bookkeeping involves systematically recording, monitoring, and administrating financial data to ensure precise accounting for your e-commerce operations.
"Does e-commerce bookkeeping truly stand apart?”
While the fundamental framework of bookkeeping remains consistent across various businesses, encompassing assets, liabilities, equity, income, and expenses, the nuances within each category, the specific considerations vital for business comprehension, and the requisite technology for accurately documenting transaction details differ from traditional brick-and-mortar or service-based enterprises.
Best Practices for E-commerce Bookkeeping
Keeping your financial records in order is crucial for any e-commerce business, no matter where you sell your products. Here are some essential tips:
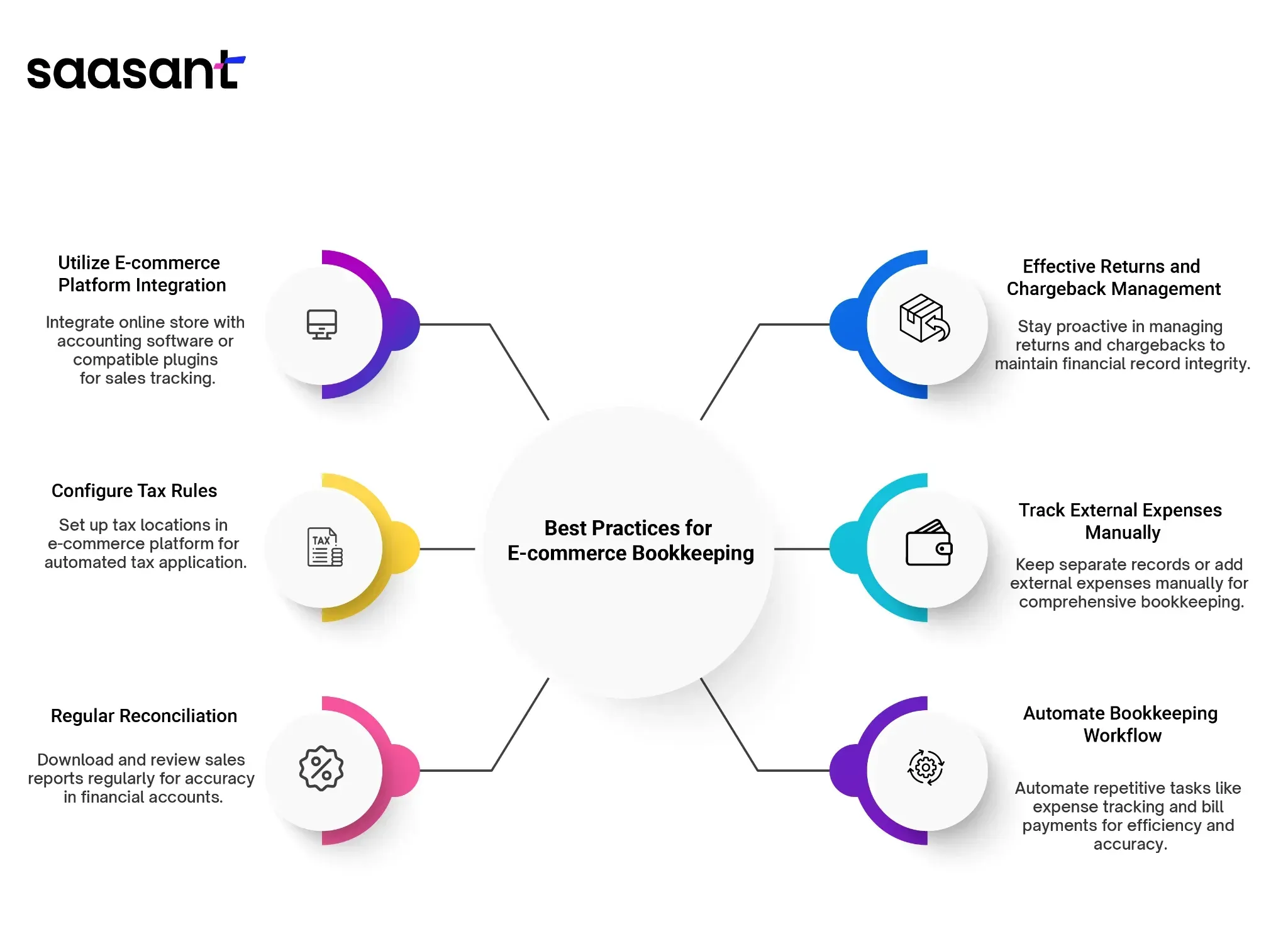
Utilize E-commerce Platform Integration
Integrate your online store with dedicated accounting software, or utilize platform-compatible plugins to track and align sales data with your accounting system.
Configure Tax Rules
Set up tax locations within your e-commerce platform to automate the application of taxes to sales where necessary. It ensures compliance and accurate tax collection based on specific geographical requirements.
Regular Reconciliation
Download and review the sales reports your e-commerce platform provides regularly. Reconcile these records to maintain accuracy and consistency in your financial accounts.
Adequate Returns and Chargeback Management
Stay proactive in managing returns and chargebacks, as they can impact your bookkeeping figures. Addressing these issues helps maintain the integrity of your financial records.
Track External Expenses Manually
Remember that your e-commerce platform may not automatically track external expenses such as staff costs, manufacturing, and advertising. Keep a separate record or add these expenses manually to ensure comprehensive bookkeeping.
Automate Bookkeeping Workflow
Simplify your bookkeeping tasks by automating repetitive processes like expense tracking, recurring bill payments, and bank reconciliation. It saves time and reduces the likelihood of errors in your financial records.
Daily, Weekly, and Monthly E-commerce Bookkeeping Tips
Daily, keeping track of receipts and maintaining a paper trail for all business activities is crucial. Whether saving the receipt from a coffee meeting with a supplier or bookmarking email receipts for digital ads, having records is vital. It helps claimre legitimate business expenses for tax benefits and avoid potential denials.
For weekly tasks, focus on monitoring your cash flow to understand how much money you have in the bank and what it needs to cover. Also, keep a close eye on any new or variable expenses, significantly if they fluctuate, to ensure they align with your expectations and business goals.
Monthly activities include reviewing your business and analyzing sales, expenses, income, and cash position. Look for trends and consider the impact of new projects or changes. Deeply examine expenses to identify opportunities for cost savings or negotiating better deals. Stay organized by categorizing receipts, whether they're in your email, Google Drive, or even that old shoebox, to streamline tax preparation and gain insights into your spending patterns.
Sales and Bookkeeping
Sales tracking is a fundamental aspect of e-commerce bookkeeping, providing insight into your company's revenue generation. Accurate recording of sales transactions ensures that income is properly documented and reconciled within financial records. This process is essential for understanding cash flow, managing accounts receivable, and assessing overall business performance.
Additionally, sales data in bookkeeping records serves as a valuable resource for analyzing sales trends, identifying top-selling products or services, and evaluating the effectiveness of marketing strategies. By maintaining detailed sales records, businesses can make informed decisions to optimize sales strategies and drive revenue growth.
Sales Tax and Bookkeeping
Sales tax is an additional charge applied to the final price when customers make online purchases, and it is typically settled during the checkout process.
It is of utmost importance to ensure that you collect sales tax if your business operates in or has a connection with a U.S. state where collecting sales tax is required, which is the case in most states. The connection or presence of your business in a state is referred to as a "nexus," and you are obligated to gather and remit sales tax for each nexus you establish.
Determine Your Nexus: Your e-commerce business establishes a presence in a state if you sell products there, store inventory, have employees, or reside in that state. Additionally, hitting a sales threshold in a specific state may create a nexus. Some states have regional sales tax that applies to out-of-state sellers.
Identify Taxable Products: Different states have varying tax rates and rules for products. Visit the official websites of each state to understand which products are subject to taxation and at what rates. Some items may not be taxable, or they may only be taxed during specific periods or seasons.
Register Your Business: Ensure compliance by obtaining a sales tax permit in any state where you have economic nexus. Depending on the state, you may also need a business permit to sell to customers within that jurisdiction.
Collect Sales Tax: Include the appropriate sales tax for each transaction; your e-commerce platform can automate this process during checkout if configured correctly.
File Tax Returns: Complete and submit tax returns within the required deadlines for the states where you must collect sales tax.
Determining Sales Tax and Recording it in Your Bookkeeping
To calculate the sales tax you need to collect and submit, follow this formula:
Sale price x Total sales tax rate = Sales tax amount
For example, if you sold an item for $100, and your city has a 2% sales tax rate while your state has a 5% rate, the combined sales tax rate is 7%.
So, 0.07 x $100 = $7
The sales tax is $7, making the final item price $107.
Ensure accurate sales tax tracking in your financial records to set aside the correct amount for taxes. One method is to debit the collected sales tax from your cash account and credit it to your sales revenue and sales tax payable accounts. It helps maintain a precise accounting of your tax obligations.
Inventory Management and Bookkeeping
Effective inventory management is pivotal in bookkeeping as it treats your inventory as a valuable asset. Maintaining control over your inventory provides clarity regarding your current stock levels, future requirements, and emerging sales patterns. This oversight lets you anticipate restocking needs, procure supplies, and modify your pricing strategy.
Managing Inventory in E-commerce Bookkeeping
To ensure your inventory remains accurate and reflects your business operations effectively, conducting monthly or quarterly updates is essential, mainly if you handle returns or manage inventory across multiple locations.
In e-commerce bookkeeping, inventory is typically tracked based on the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), and there are several calculation methods available:
FIFO (First in, First out):
This approach assumes that the items purchased or produced earliest are the ones sold or used first.
It records the oldest inventory as sold before the newer ones when calculating COGS, thus impacting profitability based on the costs of the oldest inventory.
LIFO (Last in, First out):
LIFO accounting assumes that the most recently acquired inventory is sold first.
It considers the latest purchases the first to be sold when calculating COGS, which can affect profitability as it assumes that the most recently acquired items cost more.
Average Cost Valuation:
This method calculates the average cost of all inventory items sold, regardless of when they were acquired.
It applies this average cost to all inventory items for tracking purposes.
Calculating Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and Reconcile Inventory
To compute the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) and reconcile your inventory, follow this straightforward formula:
(Beginning Inventory + Purchases) - Ending Inventory = COGS
It's essential to distinguish between COGS and your operating expenses, as they serve different purposes. COGS relates to the direct costs of producing your products, while operating expenses cover other business expenditures not directly tied to production. While both are subtracted from your total sales figures, maintain separate records for accurate financial tracking.
Payment Processing Fee and Bookkeeping
Selling online necessitates using integrated payment providers or external software for processing payments. Typically, a fee is associated with each payment transaction, and it's imperative to monitor and include these fees in your financial records.
Categorizing Payment Processing Fees
Many e-commerce enterprises classify payment processing fees as part of their Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) since they are directly linked to the costs associated with sales. To compute your gross margin, you should subtract these fees from your income.
The formula for this calculation is as follows:
Income - (COGS + Payment processing fees) = Gross profit
Financial Statement and Bookkeeping
Financial statements are crucial to e-commerce bookkeeping as they show your company's revenue, expenses, profitability, and debt. These statements play a vital role in understanding your business's financial well-being, including available funds for reinvestment, owner's compensation, and outstanding accounts payable.
Moreover, financial statements serve as valuable resources for potential investors seeking insights into your business's financial performance over time. E-commerce bookkeeping records and organizes your financial transactions, shedding light on your debits, credits, and overall business health. The data collected can then be transformed into essential financial statements, such as profit and loss statements and balance sheets.
A profit and loss statement highlights your business's revenues, costs, and expenses for a specific period. At the same time, a balance sheet provides a snapshot of your assets and liabilities at a particular moment.
Refunds and Bookkeeping
Managing refunds is an integral part of e-commerce bookkeeping, requiring accurate tracking and recording of refund transactions. Properly documenting refunds ensures that financial records reflect the adjustments in revenue and expenses accurately.
Refunds impact various aspects of bookkeeping, including accounts receivable, sales revenue, and inventory levels. Tracking refunds allows businesses to assess the impact on cash flow, analyze refund trends, and identify opportunities to improve customer satisfaction and retention.
Additionally, detailed refund records provide valuable insights into product or service performance, customer preferences, and potential areas for operational improvement. Effective management of refunds in bookkeeping contributes to maintaining financial transparency and compliance while supporting informed decision-making processes.
Fees and Bookkeeping
Incorporating fees into bookkeeping is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records and understanding the true cost of business operations. Fees can include payment processing fees, bank charges, transaction fees, and other expenses incurred during transactions.
Recording fees in bookkeeping allows businesses to track and categorize expenses effectively, providing insights into the overall cost structure and profitability. This information is essential for budgeting, financial analysis, and decision-making.
Furthermore, analyzing fee data in bookkeeping records enables businesses to identify opportunities for cost optimization, negotiate better terms with service providers, and improve cash flow management. By integrating fee management into bookkeeping practices, businesses can enhance financial transparency, compliance, and financial performance.
5 Best Applications in QuickBooks for E-commerce Bookkeeping
Running an e-commerce business requires juggling multiple hats, and managing your finances should be relatively easy. Luckily, QuickBooks offers a vast ecosystem of integrations to optimize your bookkeeping with powerful applications. Here are five must-have apps to consider for efficient e-commerce accounting:
1. Customer Management - Method: CRM
This app seamlessly integrates your customer data from QuickBooks with your existing sales and marketing tools. Gain a 360-degree view of your customers, personalize interactions, and boost sales conversions.
2. Tax Preparation and Filing - Gusto
Simplify your tax obligations with Gusto's automated payroll and tax filing. Manage payroll, pay employees and contractors, and file federal, state, and local taxes effortlessly, ensuring compliance and saving you valuable time.
3. Automated E-commerce Accounting - PayTraQer
Gain deep insights into your e-commerce operations with PayTraQer. Track sales and expenses, taxes, and fees, reconcile transactions, and manage inventory across different platforms, giving you a clear financial picture of your online store.
4. Loans, Financing, and Credit - Fundbox
Secure quick and flexible funding to fuel your business growth with Fundbox. Connect your QuickBooks data for pre-qualified loan offers and access working capital when needed without the hassle of traditional bank loans.
5. Bulk Data Importer - SaasAnt Transactions
Importing large volumes of old data can be tedious. SaasAnt Transactions automates this hectic process helping you import data from multiple platforms into your QuickBooks, saving countless hours and ensuring data accuracy.
Conclusion
Bookkeeping is the cornerstone of effective financial management for small businesses, including e-commerce. It involves systematic recording, classification, and organization of financial transactions, enabling prudent decision-making, tax compliance, and financial transparency. Neglecting bookkeeping can lead to financial woes, compliance issues, and a lack of clarity, particularly in the intricate world of e-commerce.
By establishing a proper bookkeeping system tailored to e-commerce specifics, utilizing automation applications like QuickBooks, and addressing unique challenges such as inventory management, sales tax compliance, and multi-currency transactions, businesses can ensure financial health and position themselves for success in the competitive e-commerce landscape. Bookkeeping is not just a task; it's a vital tool for growth and financial stability in the digital age.
FAQs
Should I Hire a Bookkeeper or Do My Books?
Taking on your bookkeeping requires dedicating monthly time to maintain accuracy, providing a deeper insight into your business. Alternatively, hiring a bookkeeper entails higher initial costs. Still, it offers peace of mind as a professional manage your finances, reducing the risk of errors while you focus on running your business.
What is the difference between a CPA and a bookkeeper?
A Certified Public Accountant (CPA) provides financial guidance to enhance your business's performance, whereas a bookkeeper's primary role is to keep a well-organized record of all transactions. Typically, a CPA's involvement follows the completion of bookkeeping, allowing them to analyze the data and offer valuable insights into your business's performance.
What does a bookkeeper do for a small business?
Bookkeepers handle various tasks, including processing invoices, reconciling numbers, and preparing tax documents. In this capacity, a bookkeeper assumes a pivotal role within a business, overseeing the organization of daily financial operations and providing data for future purposes, such as budgeting or fundraising.
What is the golden rule of bookkeeping?
The Three Golden Rules are
Debit for inflows, credit for outflows.
Credit for the giver, debit for the receiver.
Credit for all income, debit for all expenses.
What is double-entry bookkeeping?
Double-entry bookkeeping is a systematic method of accounting that records financial transactions by entering them into at least two different accounts, ensuring that the accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Equity) remains balanced. In this system, every transaction has a dual impact: a debit entry and a corresponding credit entry in different accounts.